Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 243-250.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.03.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical efficacy and safety of drug-eluting beads for bronchial artery chemoembolization versus conventional bronchial artery chemoembolization alone for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Huang Xingzhou1, Zheng Weihua2, Zhang Shutong2, Chen Yanhao2( )
)
- 1. Department of Radiology, Hong’an County People’s Hospital, Huanggang 438400,China
2. Department of Radiology, Wuhan Central Hospital, Tongji Medical College,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430014,China
-
Received:2024-10-17Online:2025-03-20Published:2025-03-25 -
Contact:Chen Yanhao E-mail:haohao101701@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Xingzhou, Zheng Weihua, Zhang Shutong, Chen Yanhao. Clinical efficacy and safety of drug-eluting beads for bronchial artery chemoembolization versus conventional bronchial artery chemoembolization alone for advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(3): 243-250.
share this article

Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the treatment process and efficacy evaluation of a 59-year-old female patient treated with DEB-BACE (a, b) Preoperative enhanced CT images showing central lung cancer of the right lung; (c) Diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma confirmed by percutaneous lung biopsy (H&E staining, magnification ×400 times; (d) Preoperative CT maximum density projection showing two bronchial artery blood supply; (e, f)I Intraoperative DSA images showing the involvement of two bronchial arteries for blood supply, with the staining of tumor cells; (g) Bronchial artery embolization after DSA angiography; (h, i) Plain CT scan at 6 months postoperatively showing a reduced tumor lesion, and partial remission assessed by the modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (mRECIST)
| 项目 | DEB-BACE组(n=25) | cBACE组(n=27) | t/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 67.6±8.6 | 67.3±6.7 | 0.125 | 0.901 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 16(64.0) 9(36.0) | 18(66.7) 9(33.3) | 0.410 | 0.840 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 17(68.0) 8(32.0) | 14(51.9) 13(48.1) | 1.406 | 0.236 |
| 基础疾病[例(%)] | ||||
| 高血压 | 13(52.0) | 9(33.3) | 1.853 | 0.173 |
| 2型糖尿病 | 7(28.0) | 4(14.8) | 1.353 | 0.245 |
| 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 | 8(32.0) | 7(25.9) | 0.233 | 0.629 |
| ECOG评分[例(%)] | ||||
| 0~1分 2分 | 19(76.0) 6(24.0) | 22(81.5) 5(18.5) | 0.234 | 0.629 |
| 肿瘤直径(mm) | 51.9±20.6 | 49.7±19.9 | 0.381 | 0.705 |
| 病理类型[例(%)] | ||||
| 腺癌 鳞癌 | 19(76.0) 6(24.0) | 18(66.7) 9(33.3) | 0.551 | 0.458 |
| 肿瘤分期[例(%)] | ||||
| Ⅲ期 Ⅳ期 | 6(24.0) 19(76.0) | 10(37.0) 17(63.0) | 1.036 | 0.309 |
| 肿瘤位置[例(%)] | ||||
| 中央型 周围型 | 14(56.0) 11(44.0) | 12(44.4) 15(55.6) | 0.693 | 0.405 |
| 并发症[例(%)] | ||||
| 咯血 | 8(32.0) | 10(37.0) | 0.146 | 0.703 |
| 胸腔积液 | 5(20.0) | 9(33.3) | 1.173 | 0.279 |
| 阻塞性肺炎或肺不张 | 24(96.0) | 25(92.6) | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 干预次数[例(%)] | ||||
| 1~2次 ≥3次 | 16(64.0) 9(36.0) | 21(77.8) 6(22.2) | 1.201 | 0.273 |
Tab.1 Baseline data between groups
| 项目 | DEB-BACE组(n=25) | cBACE组(n=27) | t/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 67.6±8.6 | 67.3±6.7 | 0.125 | 0.901 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 16(64.0) 9(36.0) | 18(66.7) 9(33.3) | 0.410 | 0.840 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 17(68.0) 8(32.0) | 14(51.9) 13(48.1) | 1.406 | 0.236 |
| 基础疾病[例(%)] | ||||
| 高血压 | 13(52.0) | 9(33.3) | 1.853 | 0.173 |
| 2型糖尿病 | 7(28.0) | 4(14.8) | 1.353 | 0.245 |
| 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 | 8(32.0) | 7(25.9) | 0.233 | 0.629 |
| ECOG评分[例(%)] | ||||
| 0~1分 2分 | 19(76.0) 6(24.0) | 22(81.5) 5(18.5) | 0.234 | 0.629 |
| 肿瘤直径(mm) | 51.9±20.6 | 49.7±19.9 | 0.381 | 0.705 |
| 病理类型[例(%)] | ||||
| 腺癌 鳞癌 | 19(76.0) 6(24.0) | 18(66.7) 9(33.3) | 0.551 | 0.458 |
| 肿瘤分期[例(%)] | ||||
| Ⅲ期 Ⅳ期 | 6(24.0) 19(76.0) | 10(37.0) 17(63.0) | 1.036 | 0.309 |
| 肿瘤位置[例(%)] | ||||
| 中央型 周围型 | 14(56.0) 11(44.0) | 12(44.4) 15(55.6) | 0.693 | 0.405 |
| 并发症[例(%)] | ||||
| 咯血 | 8(32.0) | 10(37.0) | 0.146 | 0.703 |
| 胸腔积液 | 5(20.0) | 9(33.3) | 1.173 | 0.279 |
| 阻塞性肺炎或肺不张 | 24(96.0) | 25(92.6) | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 干预次数[例(%)] | ||||
| 1~2次 ≥3次 | 16(64.0) 9(36.0) | 21(77.8) 6(22.2) | 1.201 | 0.273 |
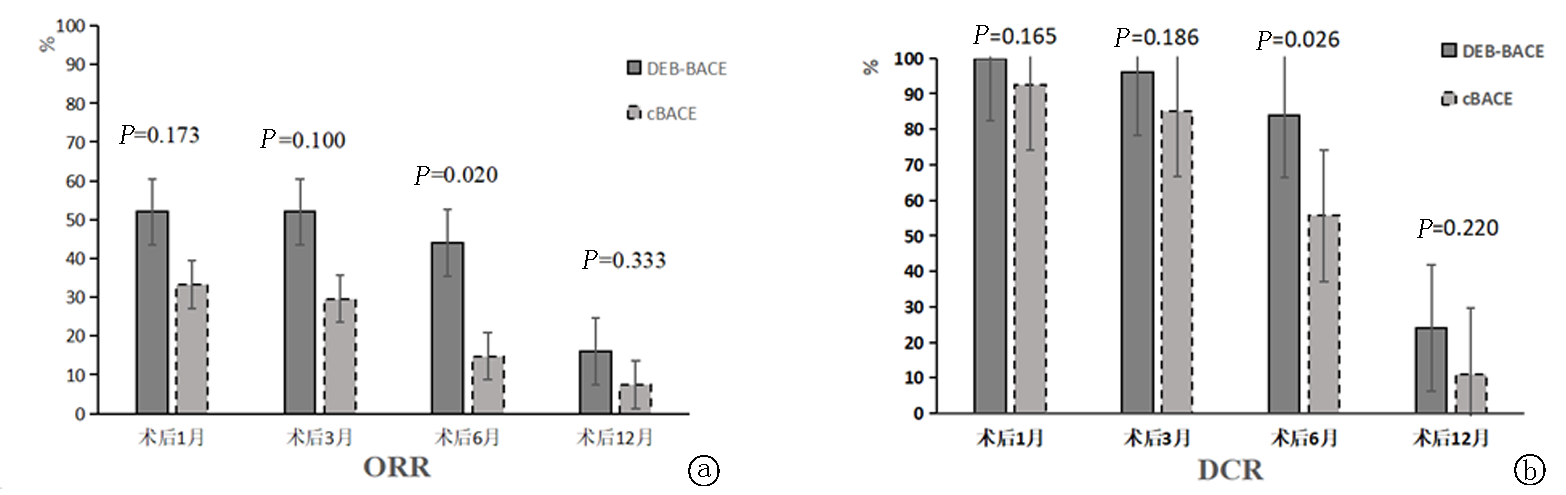
| 组别 | 例数 | 术后1月 | 术后3月 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | |||||||||||
| DEB-BACE组 | 25 | 0 | 13(52.0) | 12(48.0) | 0 | 52.0 | 100.0 | 0 | 13(52.0) | 11(44.0) | 1(4.0) | 52.0 | 96.0 | |||||||||
| cBACE组 | 27 | 0 | 9(33.3) | 16(59.3) | 2(7.4) | 33.3 | 92.6 | 0 | 8(29.6) | 15(55.6) | 4(14.8) | 29.6 | 85.2 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 术后6月 | 术后12月 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | |||||||||||
| DEB-BACE组 | 0 | 11(44.0) | 10(40.0) | 4(16.0) | 44.0 | 84.0 | 0 | 4(16.0) | 2(8.0) | 19(76.0) | 16.0 | 24.0 | ||||||||||
| cBACE组 | 0 | 4(14.8) | 11(40.7) | 12(44.4) | 14.8 | 55.6 | 0 | 2(7.4) | 1(3.7) | 24(88.9) | 7.4 | 11.1 | ||||||||||
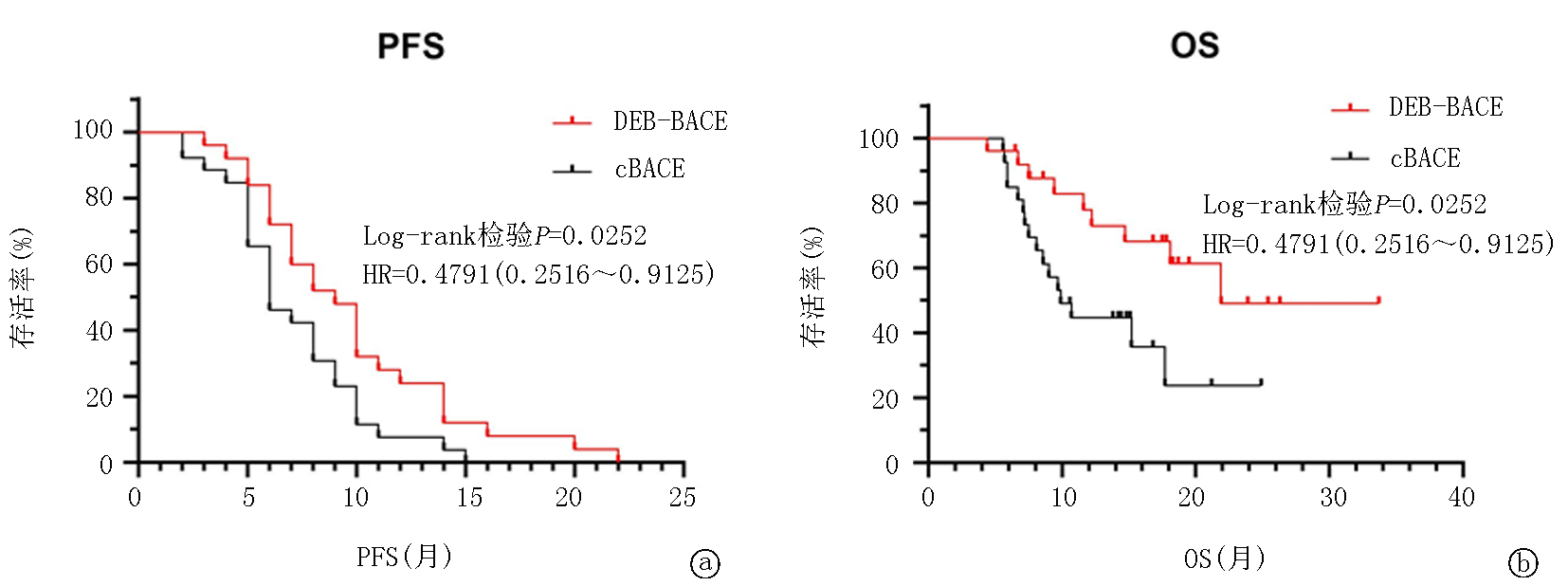
Tab.2 Comparison of clinical efficacy between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 术后1月 | 术后3月 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | |||||||||||
| DEB-BACE组 | 25 | 0 | 13(52.0) | 12(48.0) | 0 | 52.0 | 100.0 | 0 | 13(52.0) | 11(44.0) | 1(4.0) | 52.0 | 96.0 | |||||||||
| cBACE组 | 27 | 0 | 9(33.3) | 16(59.3) | 2(7.4) | 33.3 | 92.6 | 0 | 8(29.6) | 15(55.6) | 4(14.8) | 29.6 | 85.2 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 术后6月 | 术后12月 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | CR | PR [例(%)] | SD [例(%)] | PD [例(%)] | ORR (%) | DCR (%) | |||||||||||
| DEB-BACE组 | 0 | 11(44.0) | 10(40.0) | 4(16.0) | 44.0 | 84.0 | 0 | 4(16.0) | 2(8.0) | 19(76.0) | 16.0 | 24.0 | ||||||||||
| cBACE组 | 0 | 4(14.8) | 11(40.7) | 12(44.4) | 14.8 | 55.6 | 0 | 2(7.4) | 1(3.7) | 24(88.9) | 7.4 | 11.1 | ||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 发热 | 恶心呕吐 | 胸痛或胸闷 | 骨髓抑制 | 总计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEB-BACE组 | 25 | 1(4.0) | 4(16.0) | 3(12.0) | 0 | 8(32.0) |
| cBACE组 | 27 | 3(11.1) | 5(18.5) | 6(22.2) | 3(11.1) | 17(63.0) |
| χ2值 | 4.985 | |||||
| P值 | 0.026 |
Tab. 3 Incidence of adverse events between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 发热 | 恶心呕吐 | 胸痛或胸闷 | 骨髓抑制 | 总计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEB-BACE组 | 25 | 1(4.0) | 4(16.0) | 3(12.0) | 0 | 8(32.0) |
| cBACE组 | 27 | 3(11.1) | 5(18.5) | 6(22.2) | 3(11.1) | 17(63.0) |
| χ2值 | 4.985 | |||||
| P值 | 0.026 |
| [1] | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3):229-263. |
| [2] | Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2022, 2(1):1-9. |
| [3] | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(1):7-33. |
| [4] | Manzo A, Montanino A, Carillio G, et al. Angiogenesis inhibitors in NSCLC[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(10):2021. |
| [5] | 顾建平, 何旭, 陈亮, 等. 超选择性支气管动脉栓塞化疗治疗肺癌[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2003, 37(10):908-911. |
| [6] | Shang B, Li J, Wang X, et al. Clinical effect of bronchial arterial infusion chemotherapy and CalliSpheres drug-eluting beads in patients with stage Ⅱ-Ⅳ lung cancer: A prospective cohort study[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(8): 2155-2162. |
| [7] |
Han K, Yoon KW, Kim JH, et al. Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis in primary lung cancer: A retrospective review of 84 patients[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2019, 30(3): 428-434.
doi: S1051-0443(18)31444-1 pmid: 30819488 |
| [8] | Xu S, Bie ZX, Li YM, et al. Drug-eluting bead bronchialarterial chemoembolization with and without microwave ablation for the treatment of advanced and standard treatment-refractory/ineligible non-small cell lung cancer: A comparative study[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12:851830. |
| [9] | Bi Y, Li F, Ren J, et al. The safety and efficacy of oxaliplatin-loaded drugeluting beads transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable or advanced lung cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13:1079707. |
| [10] | 郭立文, 郑家平, 郝伟远, 等. 载药微球支气管动脉栓塞化疗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌10例[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2021, 30(1):24-28. |
| [11] | 王革芳. 经导管动脉灌注化疗药物应用原则——中国肿瘤介入专家共识[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2017, 26(11):963-970. |
| [12] | Cassinari M, Ugo F, Lia M, et al. Variation of serum mesothelin related proteins and of the tumor burden assessed by mRECIST criteria in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: An exploratory analysis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 493 (Suppl 1): S132-S133. |
| [13] |
Atkinson TM, Ryan SJ, Bennett AV, et al. The association between clinician-based common terminology criteria for adverse events(CTCAE) and patient-reported outcomes(PRO): A systematic review[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2016, 24(8): 3669-3676.
doi: 10.1007/s00520-016-3297-9 pmid: 27260018 |
| [14] |
Zeng Y, Yin M, Zhao Y, et al. Combination of bronchial arterial infusion chemotherapy plus drug-eluting embolic transarterial chemoembolization for treatment of advanced lung cancer-a retrospective analysis of 23 patients[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2020, 31(10):1645-1653.
doi: S1051-0443(20)30524-8 pmid: 32951974 |
| [15] | Huang R, Li WH, Zhu J, et al. Differences in efficacy between drug-eluting beads transbronchial arterial chemoembolization combined with systemic chemotherapy and systemic chemotherapy alone for unresectable lung squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2020, 100(15):1164-1168. |
| [16] | Liu XF, Lin H, Wang Q, et al. Drug-eluting bead bronchial arterial chemoembolization vs. chemotherapy in treating advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Comparison of treatment efficacy, safety and quality of life[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 25(6):2554-2566. |
| [17] | He G, Yang K, Zhang X, et al. Bronchial artery chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads versus bronchial artery infusion followed by polyvinyl alcohol particles embolization for advanced squamous cell lung cancer: A retrospective study[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2023, 161:110747. |
| [18] | Yu G, Hu J. Drug-eluting beads bronchial arterial chemoembolization as aneoadjuvant treatment for squamous non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Postgrad Med, 2020, 132(6):568-571. |
| [19] |
Lin H, Wang Q, Tian F, et al. Drug-eluting beads bronchial arterial chemoembolization in treating relapsed/refractory small cell lung cancer patients: Results from a pilot study[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2021, 13:6239-6248.
doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S310115 pmid: 34393516 |
| [20] | 赵罡, 史晓宝, 卢再鸣. Callispheres载药微球与传统支气管动脉化疗栓塞治疗不可切除的中央型鳞癌的临床疗效对比:一项回顾性研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2022, 33(6):435-440. |
| [21] | Bi Y, Shi X, Yi M, et al. Pirarubicin-loaded CalliSpheres® drug-eluting beads for the treatment of patients with stage Ⅲ-Ⅳ lung cancer[J]. Acta Radiol, 2022, 63(3):311-318. |
| [22] |
Liu X, Lin H, Wang Q, et al. Drug-eluting beads bronchial arterial chemoembolization plus intercostals arterial infusion chemotherapy is effective and well-tolerated in treating non-small cell lung cancer patients with refractory malignant pleural effusion[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2021, 13(4):2339-2350.
doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-1603 pmid: 34012583 |
| [23] | Fu Z, Wang C, Wei W, et al. Efficacy and safety of drugeluting beads bronchial arterial chemoembolization versus conventional bronchial arterial chemoembolization in lung cancer patients with hemoptysis[J]. Future Oncol, 2022, 18(25):2805-2815. |
| [24] | Xu S, Li YM, Bie ZX, et al. Drug-eluting beads bronchial arterial chemoembolization/bronchial arterial infusion chemotherapy with and without PD-1 blockade for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A comparative single-center cohort study[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2023, 13(9):6241-6256. |
| [25] | 程瑞文, 郝若冰, 李平, 等. CalliSpheres药物洗脱微球和空白微球经动脉化疗栓塞术治疗中晚期非小细胞肺癌的比较[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 32-37. |
| [26] | Yu G, Shen Y, Chen L, et al. Drug-eluting beads bronchial arterial chemoembolization vs. conventional bronchial arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2023, 10:1201468. |
| [27] | Zhu J, Zhang HP, Jiang S, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy by bronchial arterial infusion in patients with unresectable stage Ⅲ squamous cell lung cancer[J]. Ther Adv Respir Dis, 2017, 11:301-309. |
| [28] | Jin SQ, Zhao HY, Bai B, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization improves clinical efficacy and life quality of patients with lung cancer and reduces adverse reactions[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(9):10396-10403. |
| [29] | Zhao YW, Liu S, Qin H, et al. Efficacy and safety of CalliSpheres drug-eluting beads for bronchialarterial chemoembolization for refractory non-small-cell lung cancer and its impact on quality of life: A multicenter prospective study[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13:1110917. |
| [30] |
Wang Z, Niu H, Li Z, et al. Superselective arterial embolization with drug-loaded microspheres for the treatment of unresectable breast cancer[J]. Gland Surg, 2019, 8:740-747.
doi: 10.21037/gs.2019.12.06 pmid: 32042682 |
| [31] | Liu H, Li Y, Li Z, et al. Bevacizumab loaded CalliSpheres®bronchial arterial chemoembolization combined with immunotherapy and targeted therapy for advanced lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14:1170344. |
| [1] | Tang Xu, Zuo Zhuang, Yang Kai, Zhang Zhiyuan, Wang Qi, Dong Xinchun, Gou Yunjiu. The efficacy and safety of anti-angiogenic drugs combined with chemotherapy in treating malignant pleural mesothelioma: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(4): 304-312. |
| [2] | Wu Wanfeng, Wang Yunyun, Yang Daokun. Comparative study on the clinical efficacy of different antiviral drugs in the treatment of COVID-19 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 147-152. |
| [3] | Yue Jianghong, Wang Heng, Cai Gang, Zhang Xuanming, Peng Xi. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 581-592. |
| [4] | Liu Junyu, Zhang Tiancai, Zhang Baie, Li Yizhou, Li Yafei, Liu Hongbin, Duan Liping, Zhang Quanying, Wang Yijun, Meng Fanhua, Sun Min. Bioequivalence of aspirin enteric-coated tablet in healthy volunteers [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(5): 433-439. |
| [5] | Qin Qiaoling, Mo Ranghui, Chen Xinyi. Efficacy and safety of the direct-acting anti-HCV therapy based on efavirenz-containing regimen on HIV/HCV co-infected patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(10): 921-924. |
| [6] | Ma Jincai, Ma Rongzhi, Ma Zhenzhen. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban in elderly patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation complicated with cardiac insufficiency [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(5): 413-416. |
| [7] | Pan Haiyan, Qian Jing, Pan Min, Yu Xiaohong. Shortterm efficacy of ivabradine in patients with acute decompensated heart failure with reduced ejection fraction [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(4): 317-321. |
| [8] | Liang Yuling, Li Wenxi, Gu Xuewen. Randomized controlled trial of Tianma Gouteng Decoction and irbesartan in treatment of essential hypertension [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(12): 1097-1100. |
| [9] | Shi Bohan, Huang Chunmeng, Zhu Yan, Chen Zhu, Li Kunpeng, Luo Yun, Xiao Zhongxin, Tang Yanfu, Xu Qian, Xu Yan. Shortterm clinical efficacy of Kinesio Taping on walking ability of patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(12): 1111-1115. |
| [10] | Wang Na, Zhu Yugang, Liu Weiguang, Wang Defeng. Standardized antibiotic therapy for diabetic foot [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(8): 702-706. |
| [11] | Huang Debo, Mao Xianquan, Xu Zhenqiang, Feng Guokuan, Xu Fuguan, He Yuyan. Clinical efficacy of mechanical thrombectomy and intravenous thrombolysis to acute aortic occlusive stroke [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(7): 617-621. |
| [12] | Li Changqing1,2, Chai Erqing2, Jiang Lei1. Efficacy and safety of tirofiban in mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(9): 787-791,795. |
| [13] | Liu Likun, Liang Juyou, Chen Jing, Yao Yao, Guo Meng, Li Xiaona, Zhao Junli, Zhao Yiran, Xing Qiaoling, Pan Hongjuan, Li Xutong. Study on the identification of a case with blood type B(A) and the concerned clinical safety transfusion strategies [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(6): 510-514. |
| [14] | Jing Hongfei, Wang Yanfang, Wang Long. Safety and efficacy of urokinase plus tirofiban in treatment of acute ischemic stroke patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(5): 409-412. |
| [15] | Zhang Yanan1,Liu Chunxia2,Yao Xiaojian2,Zhao Li2. A case report of familially hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(9): 998-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||