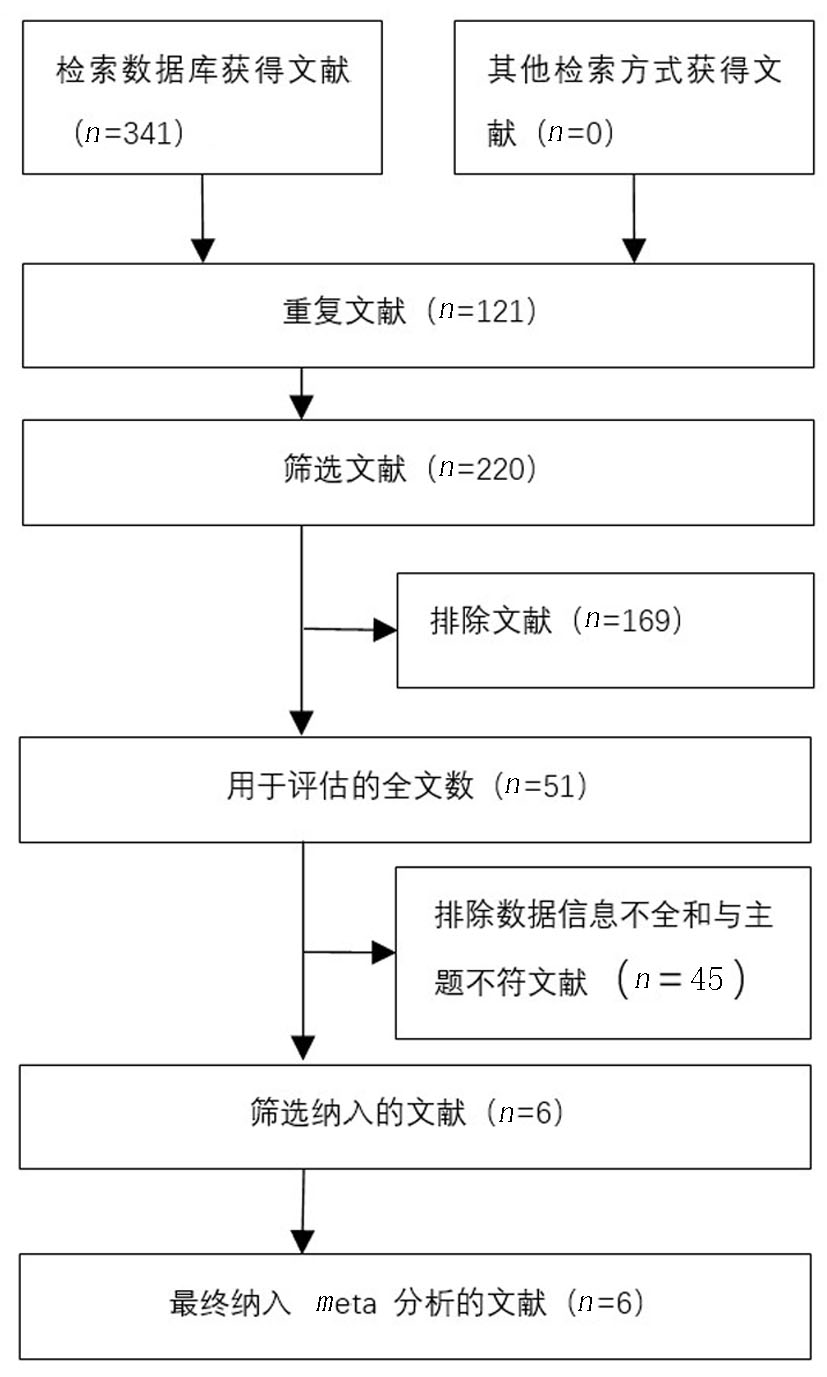
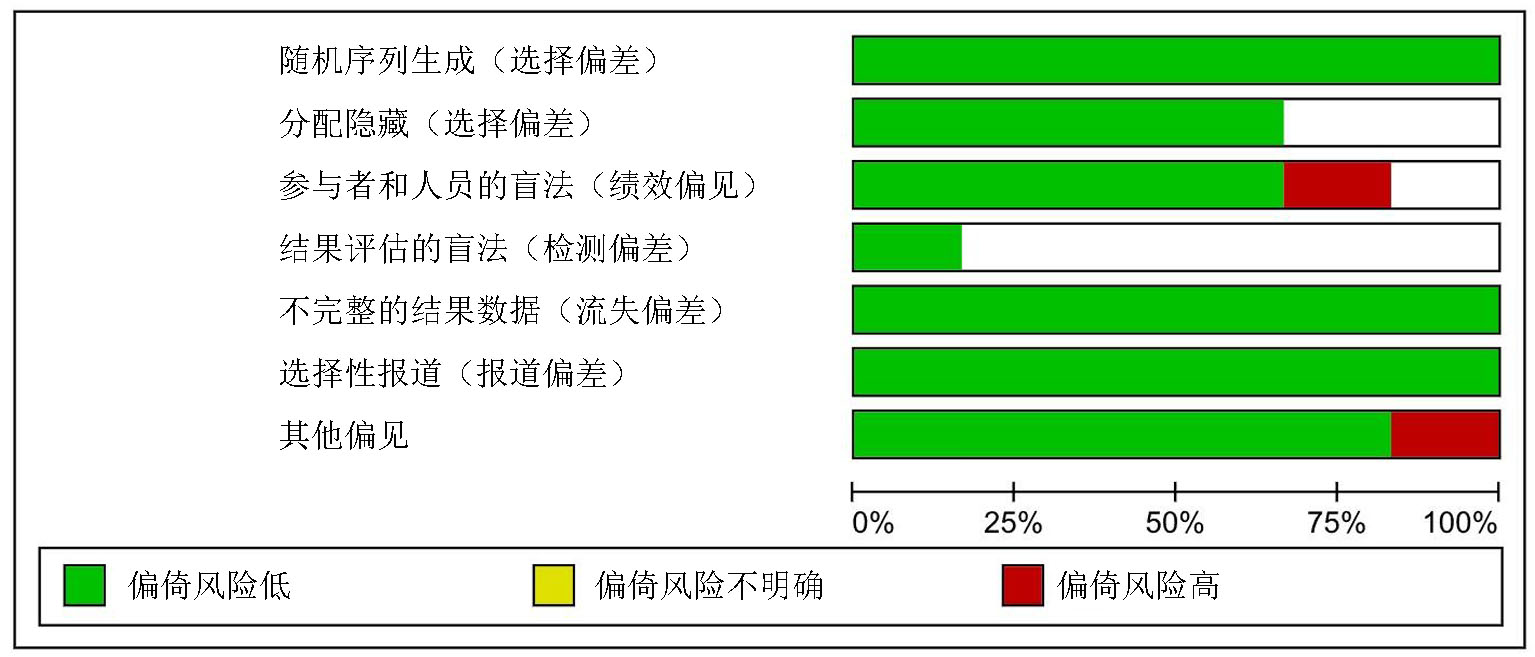
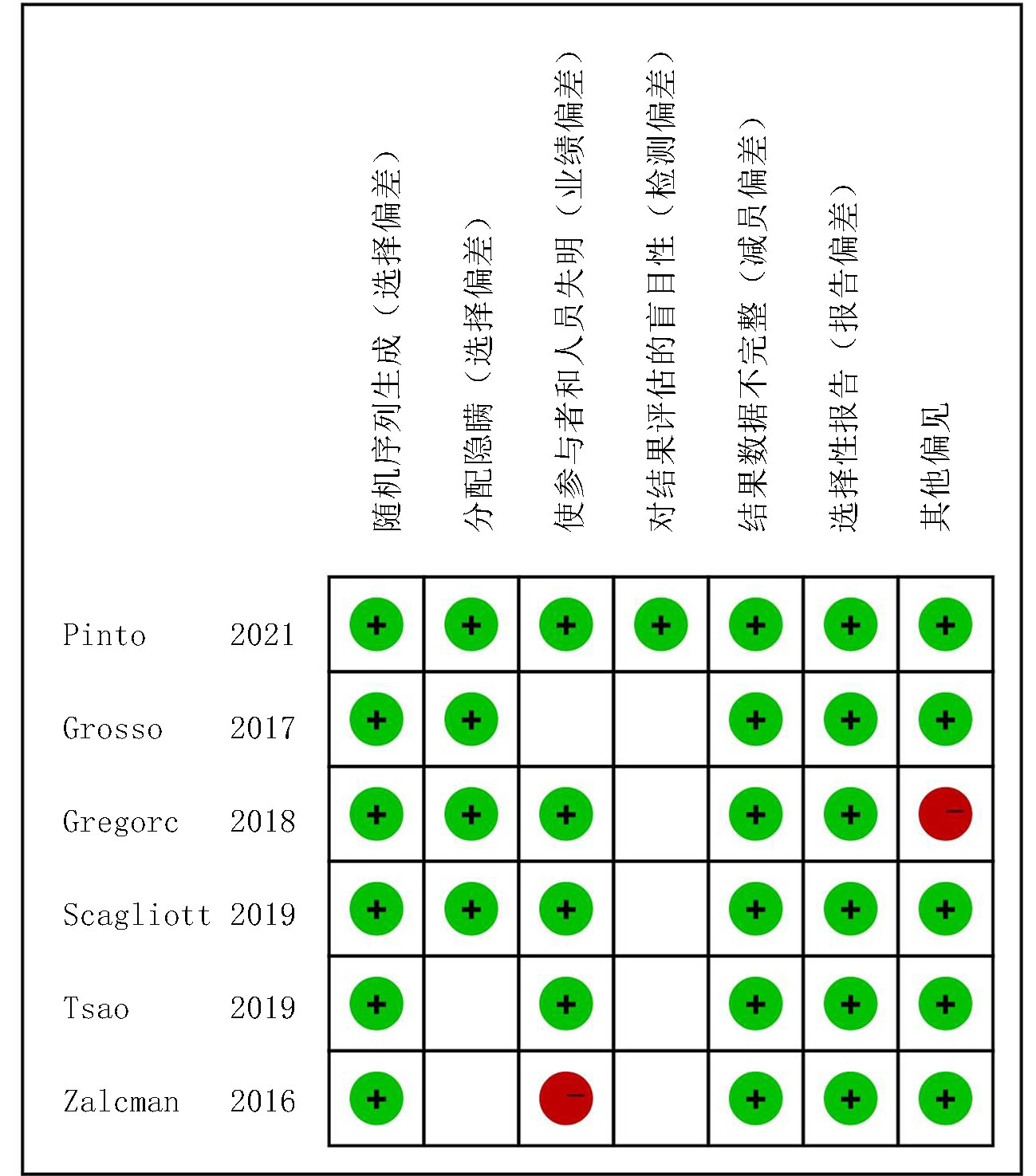
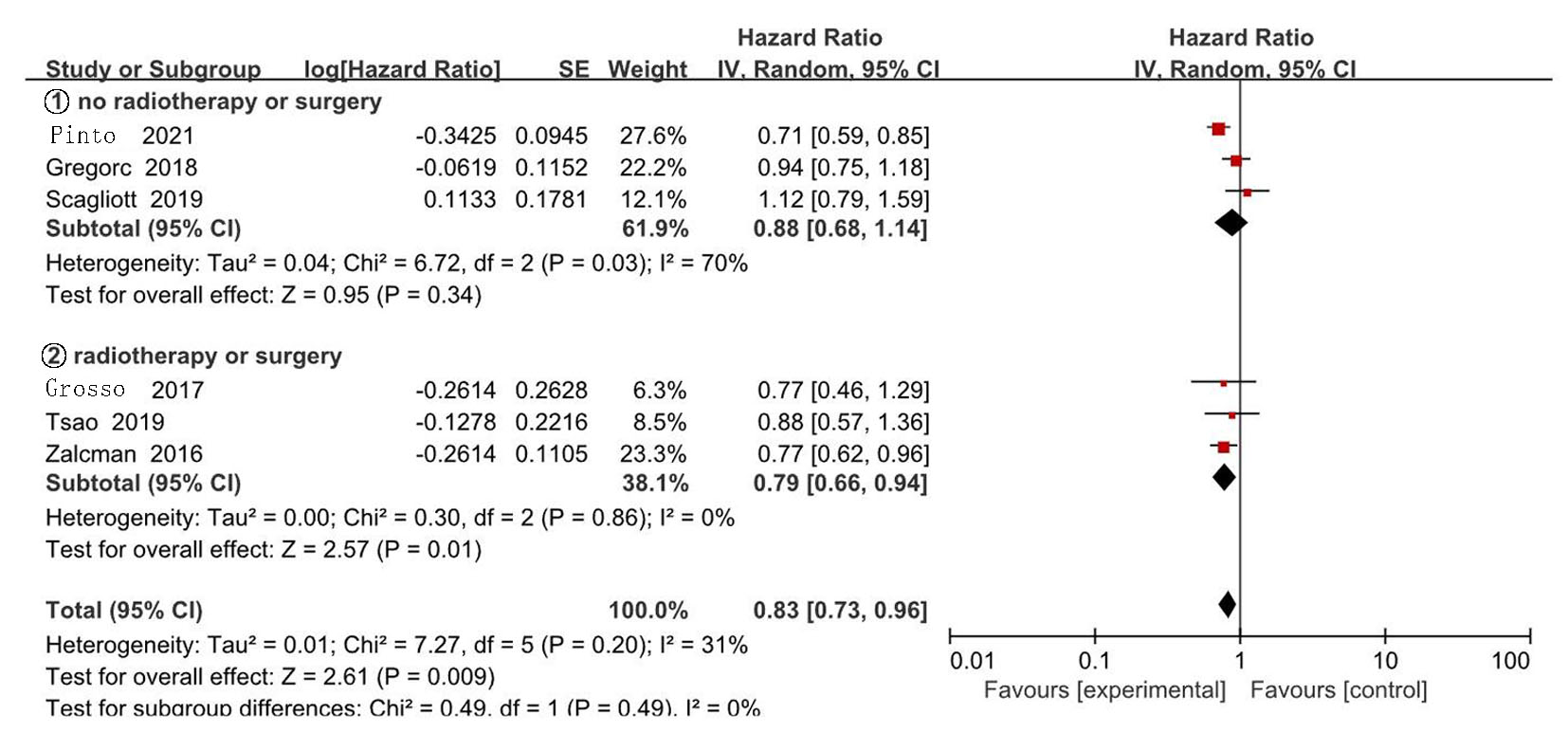
Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 304-312.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.04.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
The efficacy and safety of anti-angiogenic drugs combined with chemotherapy in treating malignant pleural mesothelioma: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Tang Xu1,2, Zuo Zhuang1,2, Yang Kai1, Zhang Zhiyuan1, Wang Qi1, Dong Xinchun1,2, Gou Yunjiu1,2( )
)
- 1.First School of Cinical M edical of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine,Lanzhou 730000,China
2.Department of Thoracic Surgery,Third Hospital of Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730000,China
-
Received:2025-02-14Online:2025-04-20Published:2025-04-17 -
Contact:Gou Yunjiu E-mail:gouyunjiu@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Xu, Zuo Zhuang, Yang Kai, Zhang Zhiyuan, Wang Qi, Dong Xinchun, Gou Yunjiu. The efficacy and safety of anti-angiogenic drugs combined with chemotherapy in treating malignant pleural mesothelioma: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(4): 304-312.
share this article
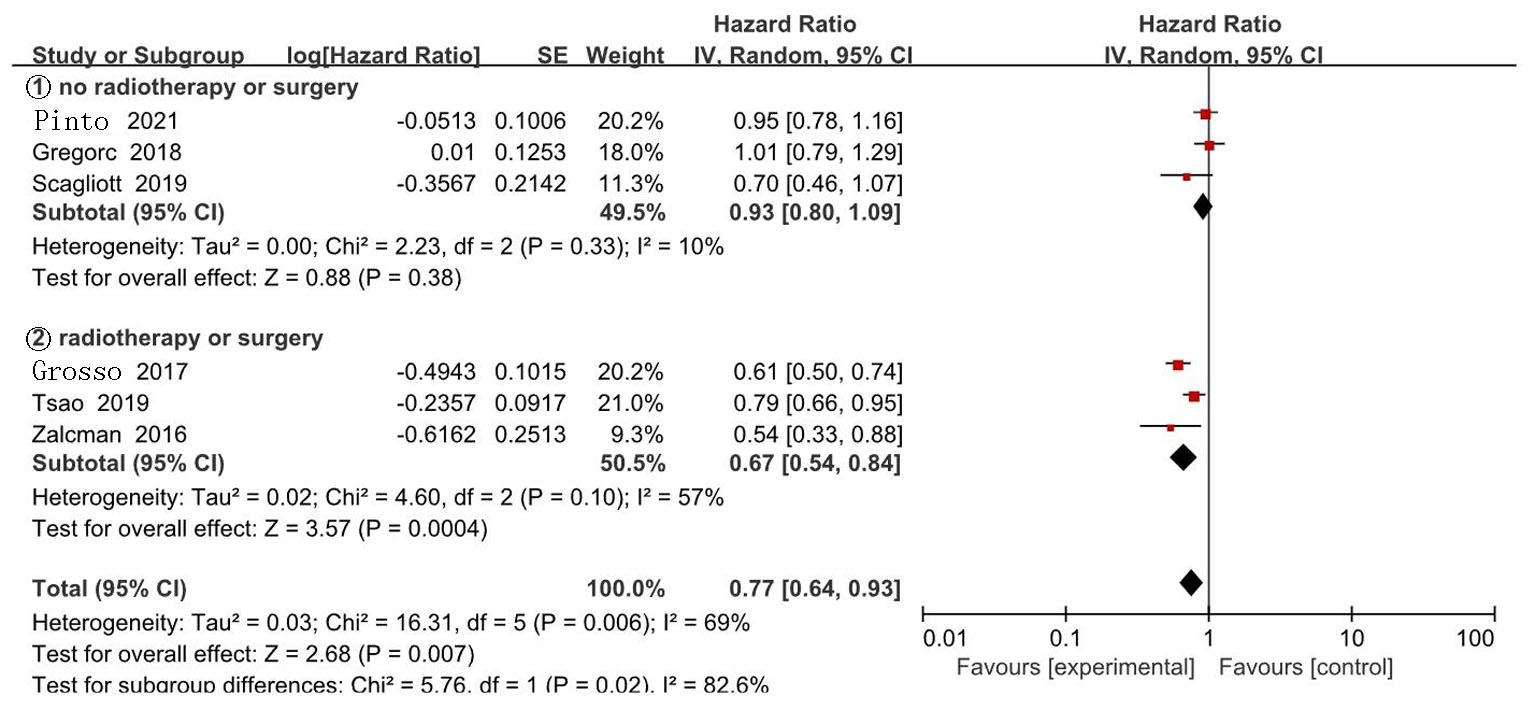
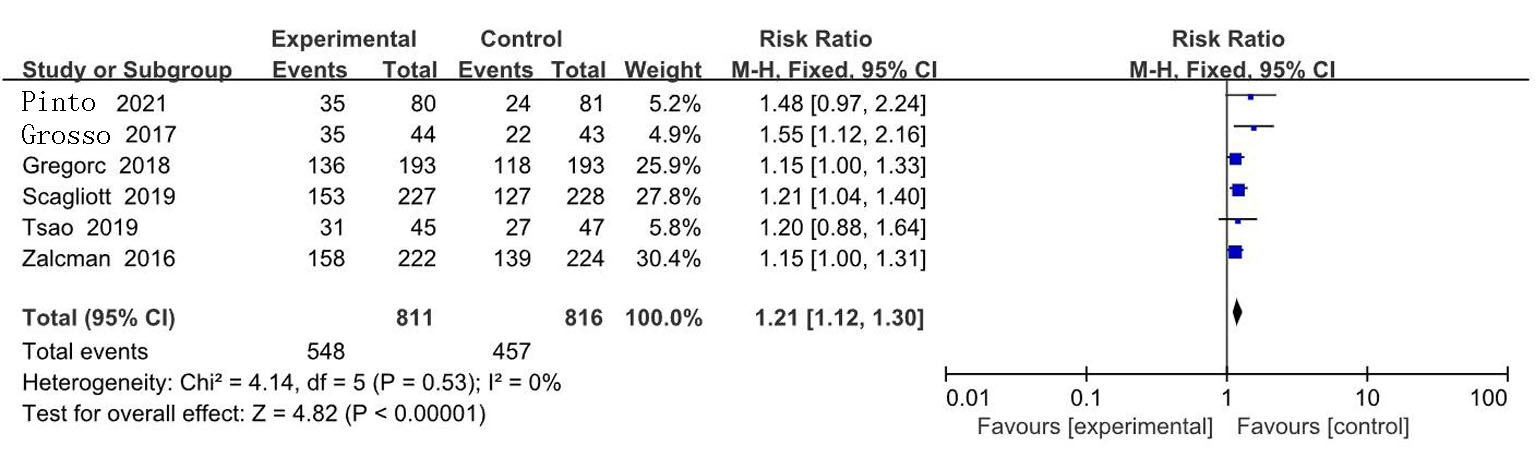
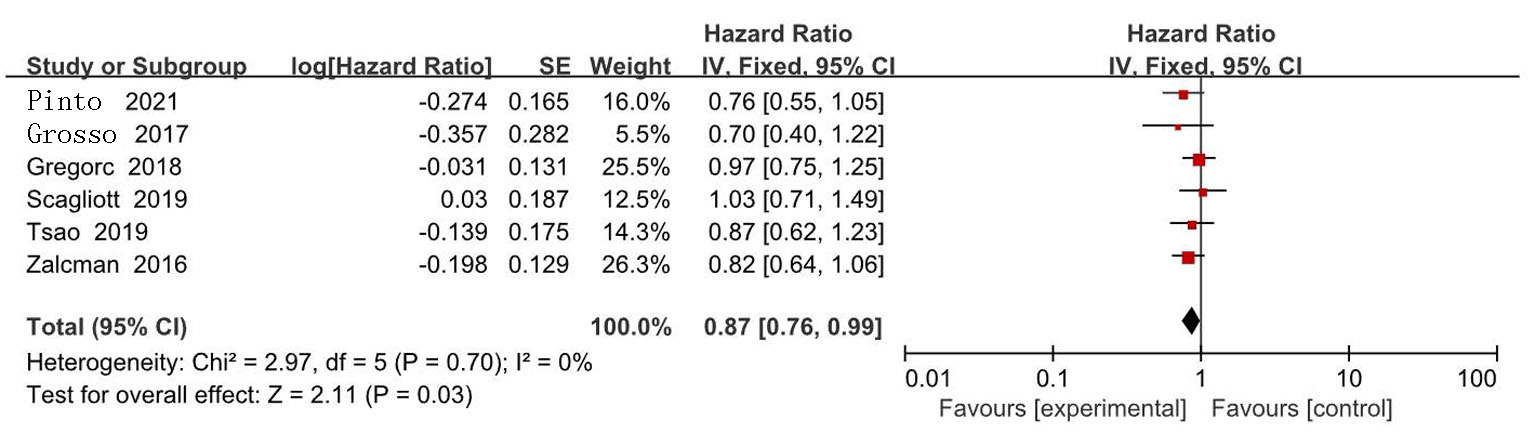
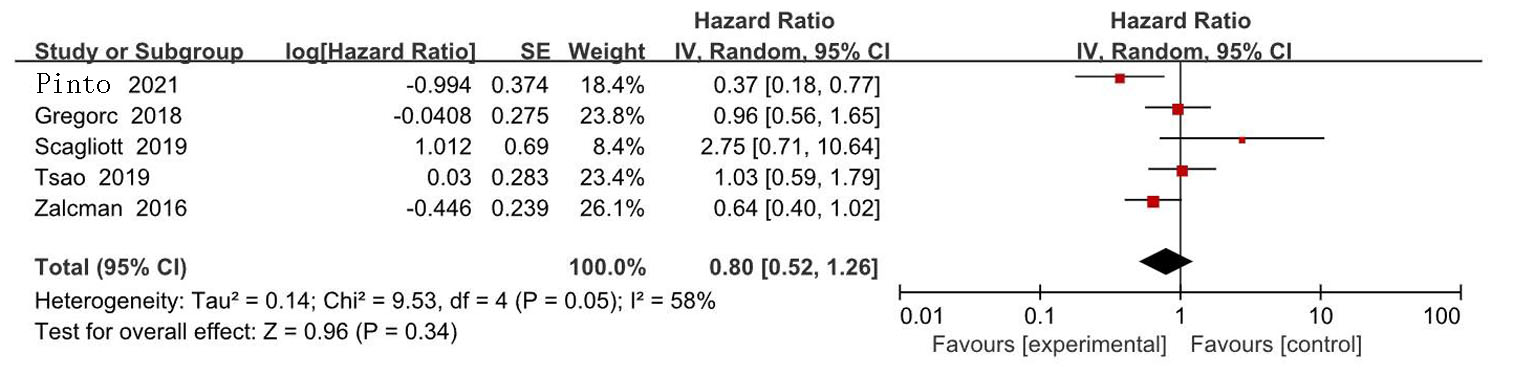
| 第一作者 | 时间 | 例数* | 治疗方式 | HR(95%CI) | 三级不良反应发生率 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 研究组 | PFS | OS | 对照组 | 研究组 | |||||
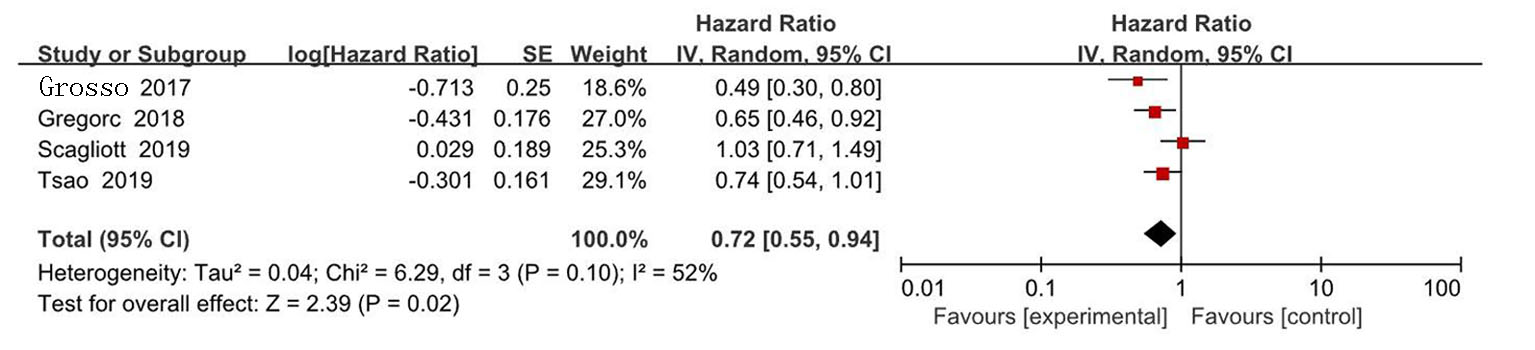
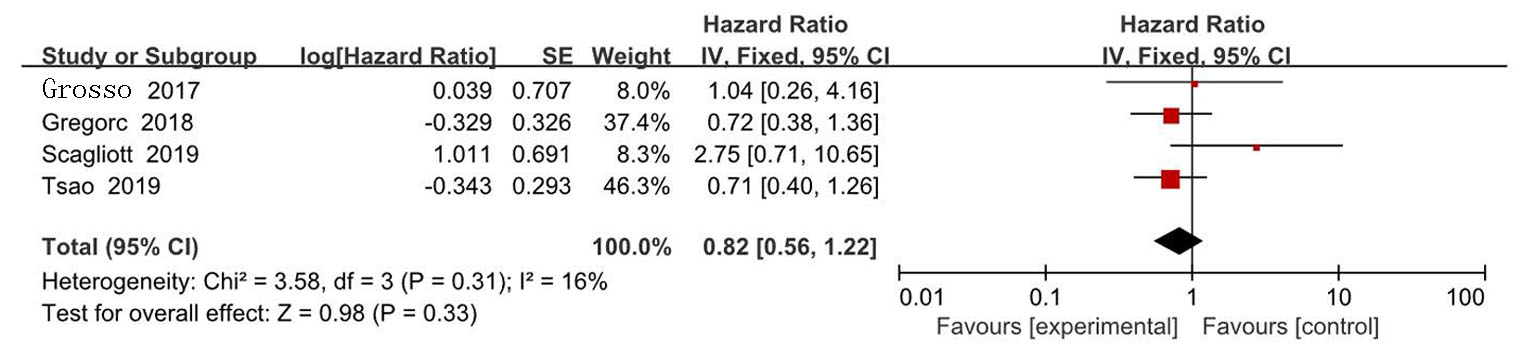
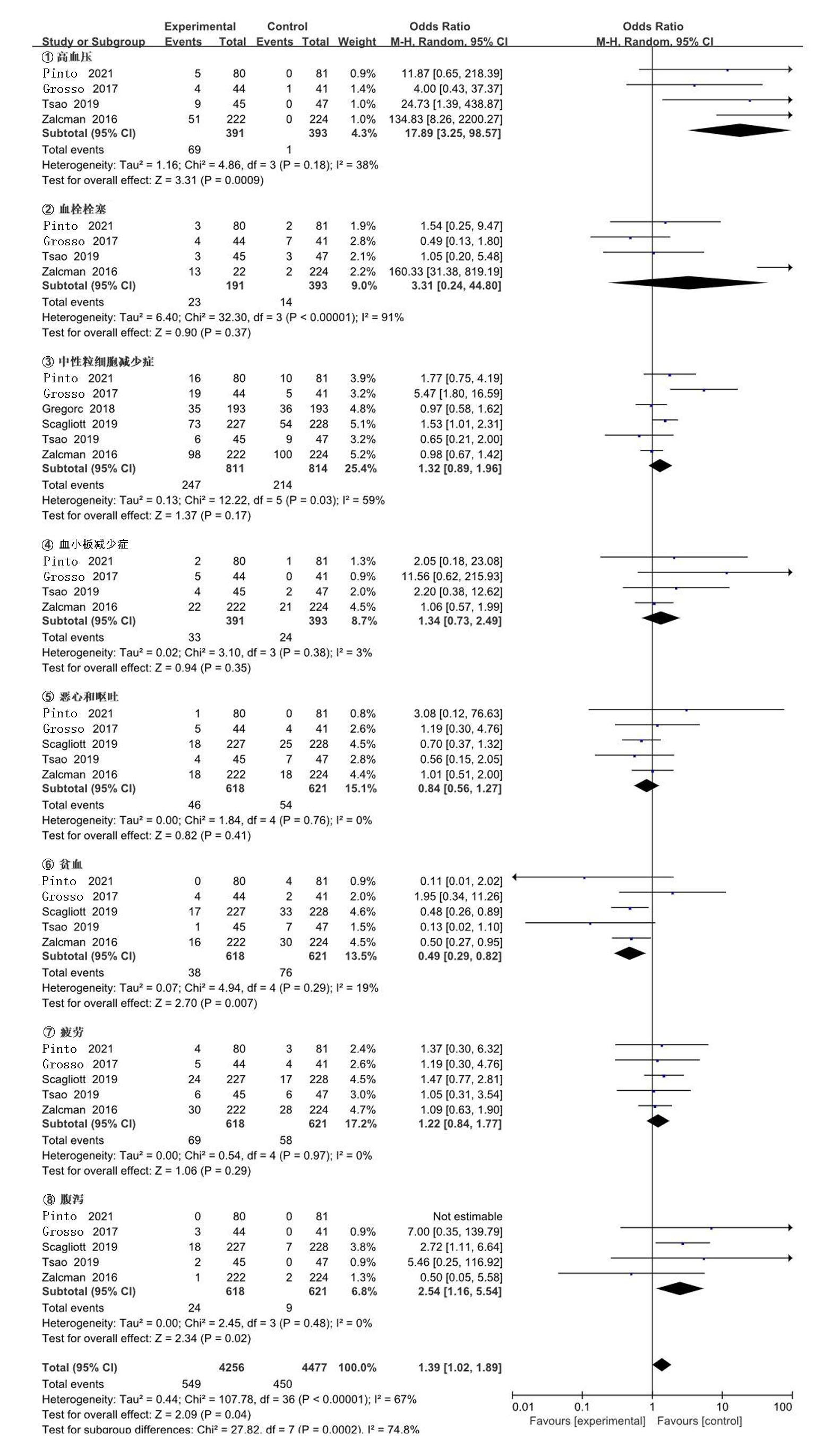
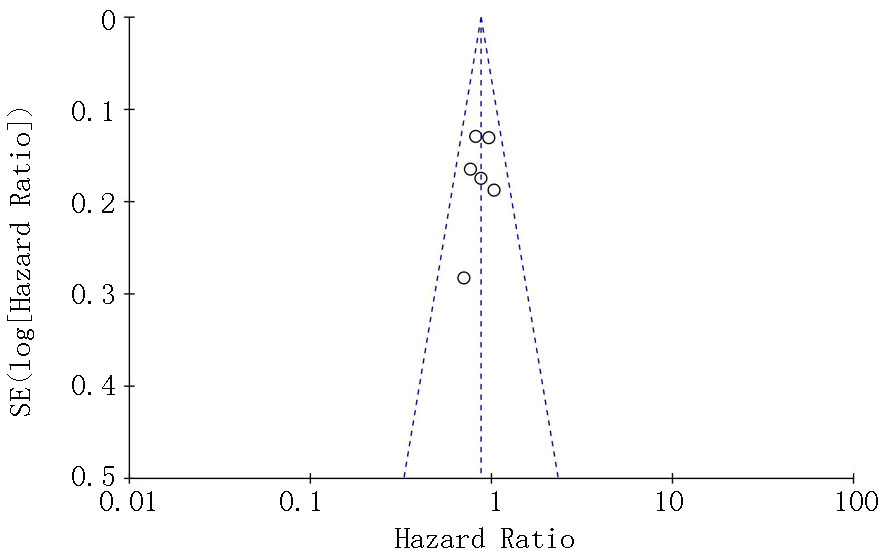
| Zalcman[ | 2016 | 223/225 | AP | 贝伐珠单抗+AP | 0.61(0.50~0.75) | 0.77(0.62~0.95) | 139/224 | 158/222 | ||
| Gregorc[ | 2018 | 193/193 | 安慰剂+最佳治疗 | NGF-hTNF+最佳治疗 | 0.95(0.78~1.17) | 0.94(0.75~1.18) | 118/193 | 136/193 | ||
| Scagliotti[ | 2019 | 229/229 | 安慰剂+AP | 尼达尼布+AP | 1.01(0.79~1.30) | 1.12(0.79~1.58) | 127/228 | 153/227 | ||
| Tsao[ | 2019 | 45/47 | 安慰剂+AP | 西地尼布+AP | 0.70(0.46~1.09) | 0.88(0.57~1.35) | 27/47 | 31/45 | ||
| Pinto[ | 2021 | 80/81 | 吉西他滨加安慰剂 | 吉西他滨+ramucirumab | 0.79(0.66~0.94) | 0.71(0.59~0.85) | 24/81 | 35/80 | ||
| Grosso[ | 2017 | 44/43 | 尼达尼布 | 培美曲塞+顺铂+尼达尼布 | 0.54(0.33~0.87) | 0.77(0.46~1.29) | 22/43 | 35/44 | ||
Tab. 1 Basic information of the included literature
| 第一作者 | 时间 | 例数* | 治疗方式 | HR(95%CI) | 三级不良反应发生率 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 研究组 | PFS | OS | 对照组 | 研究组 | |||||
| Zalcman[ | 2016 | 223/225 | AP | 贝伐珠单抗+AP | 0.61(0.50~0.75) | 0.77(0.62~0.95) | 139/224 | 158/222 | ||
| Gregorc[ | 2018 | 193/193 | 安慰剂+最佳治疗 | NGF-hTNF+最佳治疗 | 0.95(0.78~1.17) | 0.94(0.75~1.18) | 118/193 | 136/193 | ||
| Scagliotti[ | 2019 | 229/229 | 安慰剂+AP | 尼达尼布+AP | 1.01(0.79~1.30) | 1.12(0.79~1.58) | 127/228 | 153/227 | ||
| Tsao[ | 2019 | 45/47 | 安慰剂+AP | 西地尼布+AP | 0.70(0.46~1.09) | 0.88(0.57~1.35) | 27/47 | 31/45 | ||
| Pinto[ | 2021 | 80/81 | 吉西他滨加安慰剂 | 吉西他滨+ramucirumab | 0.79(0.66~0.94) | 0.71(0.59~0.85) | 24/81 | 35/80 | ||
| Grosso[ | 2017 | 44/43 | 尼达尼布 | 培美曲塞+顺铂+尼达尼布 | 0.54(0.33~0.87) | 0.77(0.46~1.29) | 22/43 | 35/44 | ||
| [1] | Sauter JL, Dacic S, Galateau-Salle F, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the pleura: Advances since the 2015 classification[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2022, 17(5): 608-622. |
| [2] | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-263. |
| [3] |
Attanoos RL, Churg A, Galateau-Salle F, et al. Malignant mesothelioma and its non-asbestos causes[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2018, 142(6): 753-760.
doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0365-RA pmid: 29480760 |
| [4] |
Nicolini F, Bocchini M, Bronte G, et al. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: State-of-the-art on current therapies and promises for the future[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 1519.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01519 pmid: 32039010 |
| [5] |
Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J, et al. Phase Ⅲ study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41(12): 2125-2133.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02542 pmid: 37068377 |
| [6] |
Zalcman G, Mazieres J, Margery J, et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10026): 1405-1414.
doi: S0140-6736(15)01238-6 pmid: 26719230 |
| [7] |
Tsao A, Nakano T, Nowak AK, et al. Targeting angiogenesis for patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Semin Oncol, 2019, 46(2): 145-154.
doi: S0093-7754(19)30060-0 pmid: 31280996 |
| [8] | Cinausero M, Rihawi K, Cortiula F, et al. Emerging therapies in malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2019, 144: 102815. |
| [9] | Disselhorst MJ, Baas P. Chemotherapy options versus “novel” therapies: how should we treat patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2020, 9(Suppl 1): S77-s85. |
| [10] |
Strizzi L, Catalano A, Vianale G, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor in human malignant mesothelioma[J]. J Pathol, 2001, 193(4): 468-475.
doi: 10.1002/path.824 pmid: 11276005 |
| [11] | Cacciotti P, Strizzi L, Vianale G, et al. The presence of simian-virus 40 sequences in mesothelioma and mesothelial cells is associated with high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2002, 26(2): 189-193. |
| [12] | 李晶, 张彩苹. 血管生成抑制剂治疗恶性胸膜间皮瘤的有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2022, 25(2): 128-132. |
| [13] |
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, et al. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis[J]. Trials, 2007, 8: 16.
pmid: 17555582 |
| [14] |
Gregorc V, Gaafar RM, Favaretto A, et al. NGR-hTNF in combination with best investigator choice in previously treated malignant pleural mesothelioma (NGR015): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2018, 19(6): 799-811.
doi: S1470-2045(18)30193-1 pmid: 29753703 |
| [15] |
Scagliotti GV, Gaafar R, Nowak AK, et al. Nintedanib in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin for chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma (LUME-Meso): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2019, 7(7): 569-580.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30139-0 pmid: 31103412 |
| [16] |
Tsao AS, Miao J, Wistuba LI, et al. Phase II trial of cediranib in combination with cisplatin and pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naïve patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (SWOG S0905)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(28): 2537-2547.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00269 pmid: 31386610 |
| [17] |
Pinto C, Zucali PA, Pagano M, et al. Gemcitabine with or without ramucirumab as second-line treatment for malignant pleural mesothelioma (RAMES): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(10): 1438-1447.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00404-6 pmid: 34499874 |
| [18] |
Grosso F, Steele N, Novello S, et al. Nintedanib plus pemetrexed/cisplatin in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Phase II results from the randomized, placebo-controlled LUME-Meso Trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35(31): 3591-600.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.9012 pmid: 28892431 |
| [19] |
Buikhuisen WA, Burgers JA, Vincent AD, et al. Thalidomide versus active supportive care for maintenance in patients with malignant mesothelioma after first-line chemotherapy (NVALT 5): An open-label, multicentre, randomised phase 3 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2013, 14(6): 543-551.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70125-6 pmid: 23583604 |
| [20] | Ohta Y, Shridhar V, Bright RK, et al. VEGF and VEGF type C play an important role in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human malignant mesothelioma tumours[J]. Br J Cancer, 1999, 81(1): 54-61. |
| [21] |
Kumar-Singh S, Vermeulen P B, Weyler J, et al. Evaluation of tumour angiogenesis as a prognostic marker in malignant mesothelioma[J]. J Pathol, 1997, 182(2): 211-216.
pmid: 9274533 |
| [22] | Chan N, Bristow R G. “Contextual” synthetic lethality and/or loss of heterozygosity: Tumor hypoxia and modification of DNA repair[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 16(18): 4553-4560. |
| [23] | 张洋, 杨帆, 王景景. 沙利度胺联合XELOX方案化疗治疗转移性结直肠癌的疗效及对生存率的影响[J]. 癌症进展, 2022, 20(7): 727-730. |
| [24] |
Howells LM, Iwuji COO, Irving GRB, et al. Curcumin combined with FOLFOX chemotherapy is safe and tolerable in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer in a randomized phase iia trial[J]. J Nutr, 2019, 149(7): 1133-1139.
doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz029 pmid: 31132111 |
| [25] | Yıldırım E, Yıldırım N, Cengiz M, et al. Protective effect of adenosine triphosphate and benidipine separately or together against cardiotoxicity caused by bevacizumab[J]. Biotech Histochem, 2023, 98(3): 193-200. |
| [26] |
Kindler HL, Karrison TG, Gandara DR, et al. Multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized phase II trial of gemcitabine/cisplatin plus bevacizumab or placebo in patients with malignant mesothelioma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2012, 30(20): 2509-2515.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.5869 pmid: 22665541 |
| [27] |
Gad ES, Salama AAA, El-Shafie MF, et al. The anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and nintedanib in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats[J]. Inflammation, 2020, 43(1): 123-134.
doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01101-2 pmid: 31646446 |
| [28] | Fan Y, Li X, Fang X, et al. Antifibrotic role of nintedanib in tracheal stenosis after a tracheal wound[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(9): E2496-e505. |
| [29] |
Wozniak AJ, Schneider B, Kalemkerian GP, et al. Short report of a phase ii trial of nintedanib in recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM)[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2023, 24(6): 563-567.
doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2023.04.004 pmid: 37301693 |
| [30] |
Randall LM, Monk BJ. Bevacizumab toxicities and their management in ovarian cancer[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2010, 117(3): 497-504.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.02.021 pmid: 20363017 |
| [1] | Huang Xingzhou, Zheng Weihua, Zhang Shutong, Chen Yanhao. Clinical efficacy and safety of drug-eluting beads for bronchial artery chemoembolization versus conventional bronchial artery chemoembolization alone for advanced non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(3): 243-250. |
| [2] | Yue Jianghong, Wang Heng, Cai Gang, Zhang Xuanming, Peng Xi. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 581-592. |
| [3] | Liu Junyu, Zhang Tiancai, Zhang Baie, Li Yizhou, Li Yafei, Liu Hongbin, Duan Liping, Zhang Quanying, Wang Yijun, Meng Fanhua, Sun Min. Bioequivalence of aspirin enteric-coated tablet in healthy volunteers [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(5): 433-439. |
| [4] | Qin Qiaoling, Mo Ranghui, Chen Xinyi. Efficacy and safety of the direct-acting anti-HCV therapy based on efavirenz-containing regimen on HIV/HCV co-infected patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(10): 921-924. |
| [5] | Li Hai, Liu Wenhu, Peng Shaopeng, Wang Fei. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of controlled stepwise decompression versus rapid standard large bone-flap decompression on the treatment of severe craniocerebral injury [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(9): 788-795. |
| [6] | Wang Tengyan, He Yajun, Shu Jianchang. Rebamipide in the treatment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated intestinal disease: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(8): 685-690. |
| [7] | Li Shufan, Wang Yuxiu, Jiang Zhenghua. The correlation between the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma with acquired resistance to the first-generation EGFR TKI and the T790M mutation [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(11): 985-991. |
| [8] | Ma Jincai, Ma Rongzhi, Ma Zhenzhen. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban in elderly patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation complicated with cardiac insufficiency [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(5): 413-416. |
| [9] | Xi Lingyan1, Huang Xiuqin1, Zhang Suyun1, Li Ziyu1, Xu Congen1, Jin Guixing2. The efficacy and safety of assessmentbased treatment models in patients with schizophrenia [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(6): 530-534. |
| [10] | Feng Junshuai, Fu Caihong, Ma Ru, Zhou Qianqian, Zhou Huiru, Zhang Jinzhou, Gao Junlong, Wang Xiandong. Efficacy of plasma diafiltration in treatment of hepatic failure complicated with sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(4): 330-333. |
| [11] | Zhang Kaixuan1, Geng Wei2, Jiang Yiming1, Wang Xueshuo1, Hou Xuena1. Effect of Qishenyiqi dropping pill on heart failure with preserved ejection fraction [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(11): 995-998. |
| [12] | Li Changqing1,2, Chai Erqing2, Jiang Lei1. Efficacy and safety of tirofiban in mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(9): 787-791,795. |
| [13] | Liu Likun, Liang Juyou, Chen Jing, Yao Yao, Guo Meng, Li Xiaona, Zhao Junli, Zhao Yiran, Xing Qiaoling, Pan Hongjuan, Li Xutong. Study on the identification of a case with blood type B(A) and the concerned clinical safety transfusion strategies [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(6): 510-514. |
| [14] | Jing Hongfei, Wang Yanfang, Wang Long. Safety and efficacy of urokinase plus tirofiban in treatment of acute ischemic stroke patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(5): 409-412. |
| [15] | Wang Mina, Gao Weib, Hu Xiaoweia, Wu Chaob, Xu Mina. Preoperative localization and surgical outcome analysis of multifocal refractory epilepsy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(12): 1031-1035. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||