Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 237-242.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.03.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical value of combined serum biomarker detection for early prediction of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome
Feng Yuhui, Zou Lanlan, Cui Chenhang, Huang Xianjie, Qiao Junying( )
)
- Department of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
-
Received:2024-12-22Online:2025-03-20Published:2025-03-25 -
Contact:Qiao Junying E-mail:junying.qiao@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Yuhui, Zou Lanlan, Cui Chenhang, Huang Xianjie, Qiao Junying. Clinical value of combined serum biomarker detection for early prediction of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(3): 237-242.
share this article
| 指标 | pARDS组(n=35) | 非pARDS组(n=57) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(月) | 9.80(2.77, 12.50) | 10.37(2.02, 18.00) | Z=0.076 | 0.939 |
| 体重(kg) | 8.20(5.00, 10.50) | 8.50(4.00, 10.00) | Z=1.127 | 0.260 |
| 男性[例(%)] | 24(68.6) | 34(59.6) | χ2=0.741 | 0.389 |
| 白细胞(×109/L) | 10.84(6.74, 14.77) | 9.61(6.55, 15.73) | Z=0.197 | 0.844 |
| 血小板(×109/L) | 350(257, 523) | 314(236, 441) | Z=0.993 | 0.321 |
| 肌酐( μmol/L) | 20.30(16.70, 26.00) | 18.80(16.00, 23.44) | Z=0.768 | 0.442 |
| D-二聚体(mg/L) | 0.35(0.27, 0.60) | 0.47(0.28, 1.09) | Z=1.693 | 0.090 |
| 总蛋白(g/L) | 57.38±8.26 | 55.30±10.41 | t=1.005 | 0.318 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 35.57±6.12 | 34.83±6.98 | t=0.519 | 0.605 |
| PCIS评分(分) | 80.17±4.93 | 82.60±4.39 | t=2.453 | 0.016 |
| 机械通气时长(h) | 199(150, 277) | 104 (29, 131) | Z=5.825 | 0.000 |
| 住院天数(d) | 23.00(17.00, 27.00) | 18.00(13.00, 27.50) | Z=1.787 | 0.074 |
| 原发疾病[例(%)] | χ2=3.661 | 0.300 | ||
| 肺炎 | 20(57.1) | 29(50.9) | ||
| 脓毒症 | 9(25.7) | 9(15.8) | ||
| 大手术术后 | 4(11.4) | 15(26.3) | ||
| 其他 | 2(5.7) | 4(7.0) |
Tab.1 General clinical data between the two groups
| 指标 | pARDS组(n=35) | 非pARDS组(n=57) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(月) | 9.80(2.77, 12.50) | 10.37(2.02, 18.00) | Z=0.076 | 0.939 |
| 体重(kg) | 8.20(5.00, 10.50) | 8.50(4.00, 10.00) | Z=1.127 | 0.260 |
| 男性[例(%)] | 24(68.6) | 34(59.6) | χ2=0.741 | 0.389 |
| 白细胞(×109/L) | 10.84(6.74, 14.77) | 9.61(6.55, 15.73) | Z=0.197 | 0.844 |
| 血小板(×109/L) | 350(257, 523) | 314(236, 441) | Z=0.993 | 0.321 |
| 肌酐( μmol/L) | 20.30(16.70, 26.00) | 18.80(16.00, 23.44) | Z=0.768 | 0.442 |
| D-二聚体(mg/L) | 0.35(0.27, 0.60) | 0.47(0.28, 1.09) | Z=1.693 | 0.090 |
| 总蛋白(g/L) | 57.38±8.26 | 55.30±10.41 | t=1.005 | 0.318 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 35.57±6.12 | 34.83±6.98 | t=0.519 | 0.605 |
| PCIS评分(分) | 80.17±4.93 | 82.60±4.39 | t=2.453 | 0.016 |
| 机械通气时长(h) | 199(150, 277) | 104 (29, 131) | Z=5.825 | 0.000 |
| 住院天数(d) | 23.00(17.00, 27.00) | 18.00(13.00, 27.50) | Z=1.787 | 0.074 |
| 原发疾病[例(%)] | χ2=3.661 | 0.300 | ||
| 肺炎 | 20(57.1) | 29(50.9) | ||
| 脓毒症 | 9(25.7) | 9(15.8) | ||
| 大手术术后 | 4(11.4) | 15(26.3) | ||
| 其他 | 2(5.7) | 4(7.0) |
| 指标 | 例数 | KL-6 (ng/ml) | IL-8 (pg/ml) | vWF (μg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pARDS组 | 35 | 3.33(2.44, 4.05) | 45.39(33.94, 65.30) | 5.81±1.53 |
| 非pARDS组 | 57 | 2.13(1.50, 2.68) | 36.74(19.21, 48.95) | 4.86±2.12 |
| 统计值 | Z=3.993 | Z=2.598 | t=2.489 | |
| P值 | 0 | 0.009 | 0.015 |
Tab.2 The serum marker levels between the two groups at T1
| 指标 | 例数 | KL-6 (ng/ml) | IL-8 (pg/ml) | vWF (μg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pARDS组 | 35 | 3.33(2.44, 4.05) | 45.39(33.94, 65.30) | 5.81±1.53 |
| 非pARDS组 | 57 | 2.13(1.50, 2.68) | 36.74(19.21, 48.95) | 4.86±2.12 |
| 统计值 | Z=3.993 | Z=2.598 | t=2.489 | |
| P值 | 0 | 0.009 | 0.015 |
| KL-6 (ng/ml) | IL-8 (pg/ml) | vWF (μg/ml) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 3.33(2.44, 4.05) | 45.39(33.94, 65.30) | 5.81±1.53 |
| T2 | 5.19(3.02, 6.72)* | 76.24(45.71, 109.75)* | 6.72±1.94* |
| T3 | 6.47(5.11, 8.47)# | 53.78(36.19, 76.87)# | 5.66±1.71# |
| 统计值 | H=36.289 | H=10.006 | F=3.824 |
| P值 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.025 |
Tab.3 The serum markers in pARDS group at different time points
| KL-6 (ng/ml) | IL-8 (pg/ml) | vWF (μg/ml) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 3.33(2.44, 4.05) | 45.39(33.94, 65.30) | 5.81±1.53 |
| T2 | 5.19(3.02, 6.72)* | 76.24(45.71, 109.75)* | 6.72±1.94* |
| T3 | 6.47(5.11, 8.47)# | 53.78(36.19, 76.87)# | 5.66±1.71# |
| 统计值 | H=36.289 | H=10.006 | F=3.824 |
| P值 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.025 |
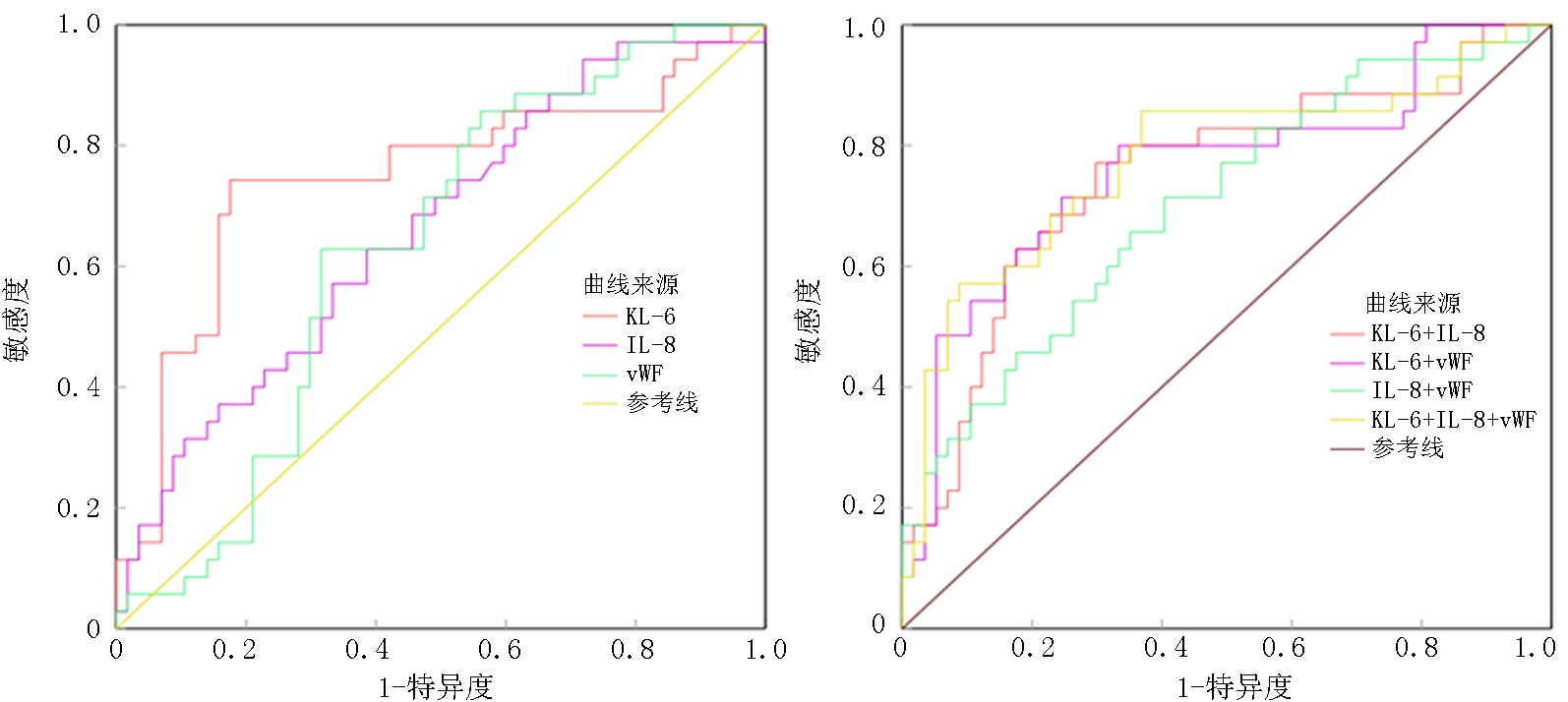
| 指标 | AUC | 95%可信区间 | 截断值 | 敏感度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL-6 | 0.749 | 0.637~0.861 | 2.727 | 74.3 | 82.5 |
| IL-8 | 0.662 | 0.549~0.775 | 41.072 | 62.9 | 61.4 |
| vWF | 0.631 | 0.518~0.745 | 5.850 | 62.9 | 68.4 |
| KL-6+IL-8 | 0.751 | 0.644~0.858 | - | 77.1 | 70.2 |
| KL-6+vWF | 0.762 | 0.655~0.869 | - | 71.4 | 75.4 |
| IL-8+vWF | 0.703 | 0.593~0.813 | - | 71.4 | 59.6 |
| KL-6+IL-8+vWF | 0.776 | 0.671~0.882 | - | 85.7 | 63.2 |
Tab.4 Efficacy evaluation of serum markers in the early prediction of pARDS
| 指标 | AUC | 95%可信区间 | 截断值 | 敏感度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL-6 | 0.749 | 0.637~0.861 | 2.727 | 74.3 | 82.5 |
| IL-8 | 0.662 | 0.549~0.775 | 41.072 | 62.9 | 61.4 |
| vWF | 0.631 | 0.518~0.745 | 5.850 | 62.9 | 68.4 |
| KL-6+IL-8 | 0.751 | 0.644~0.858 | - | 77.1 | 70.2 |
| KL-6+vWF | 0.762 | 0.655~0.869 | - | 71.4 | 75.4 |
| IL-8+vWF | 0.703 | 0.593~0.813 | - | 71.4 | 59.6 |
| KL-6+IL-8+vWF | 0.776 | 0.671~0.882 | - | 85.7 | 63.2 |
| [1] |
Goodman D, Crocker ME, Pervaiz F, et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of paediatric pneumonia in intervention field trials: Recommendations from a pneumonia field trial working group[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2019, 7(12): 1068-1083.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30249-8 pmid: 31591066 |
| [2] | 原静, 李书芳, 郎元法. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征儿童的临床特征研究[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2024, 19(3): 374-378. |
| [3] | Emeriaud G, López-Fernández YM, Iyer NP, et al. Executive summary of the second international guidelines for the diagnosis and management of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (PALICC-2)[J]. Pediatr Crit Care Med, 2023, 24(2): 143-168. |
| [4] |
Guérin C, Thompson T, Brower R. The ten diseases that look like ARDS[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2015, 41(6): 1099-1102.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3608-x pmid: 25527375 |
| [5] | Kalbhenn J, Glonnegger H, Wilke M, et al. Hypercoagulopathy, acquired coagulation disorders and anticoagulation before, during and after extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in COVID-19: A case series[J]. Perfusion, 2021, 36(6): 592-602. |
| [6] | Williams JG, Jones RL, Yunger TL, et al. Comparison of 16 pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome-associated plasma biomarkers with changing lung injury severity[J]. Pediatr Crit Care Med, 2024, 25(1): e31-e40. |
| [7] |
Carlton EF, Flori HR. Biomarkers in pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2019, 7(19): 505.
doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.29 pmid: 31728358 |
| [8] |
Matthay MA, Zemans RL, Zimmerman GA, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2019, 5(1): 18.
doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0069-0 pmid: 30872586 |
| [9] | 曾宪飞, 卢东雪, 张西京, 等. 5种血清学标志物对急性呼吸窘迫综合征的诊断和预后预测价值[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 40(4): 588-592,618. |
| [10] | Jiang LN, Shao CL, Jiang WJ, et al. Advanced research of KL-6 in respiratory diseases[J]. Int J Respir, 2019, 39(21): 1665-1669. |
| [11] | Aisiku IP, Yamal JM, Doshi P, et al. Plasma cytokines IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 are associated with the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with severe traumatic brain injury[J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20: 288. |
| [12] |
Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition[J]. JAMA, 2012, 307(23): 2526-2533.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.5669 pmid: 22797452 |
| [13] | 张涛, 刘春峰. 2023版国际儿童急性呼吸窘迫综合征诊疗指南解读[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2023, 30(11): 801-808. |
| [14] | 高杨, 李军. 生物标志物联合应用在急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者诊断及预后评估中的意义[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2021, 33(1): 69-73. |
| [15] |
Han L, Wang S, Ma J, et al. Expression and significance of serum KL-6 in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2023, 15(12): 6988-6995.
doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1787 pmid: 38249915 |
| [16] | 宗晓龙, 李真玉, 魏殿军, 等. 肺泡表面活性蛋白D、血管性血友病因子及白介素8对脓毒症诱发急性呼吸窘迫综合征的预测和预后意义[J]. 临床检验杂志, 2017, 35(2): 118-121. |
| [17] |
Whitney JE, Feng R, Koterba N, et al. Endothelial biomarkers are associated with indirect lung injury in sepsis-associated pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Crit Care Explor, 2020, 2(12): e0295.
doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000295 pmid: 33299985 |
| [18] | 何琛璐, 王雪君, 刘润武, 等. 血清vWF:Ag、Claudin-5及sTM联合检测在ARDS患儿早期诊断及预后评估中的应用[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2021, 42(21): 2614-2618. |
| [19] | 孙夏烨, 朱晓东. 小儿急性肺损伤及其生物标记物研究进展[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2015, 22 (2): 140-142. |
| [20] | van der Zee P, Rietdijk W, Somhorst P, et al. A systematic review of biomarkers multivariately associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome development and mortality[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1): 243. |
| [21] | 李双凤, 高延秋, 李晓燕, 等. EVLWI、sICAM-1和KL-6联合检测在重症肺炎ARDS患者预后评估中的价值[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2021, 30(6): 730-736. |
| [22] | 王丽阳, 王艺璁, 刘欢, 等. 血清RAGE、PBEF水平对重症肺炎患儿继发急性呼吸窘迫综合征的预测价值[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2024, 23(9):1085-1089+1099. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||