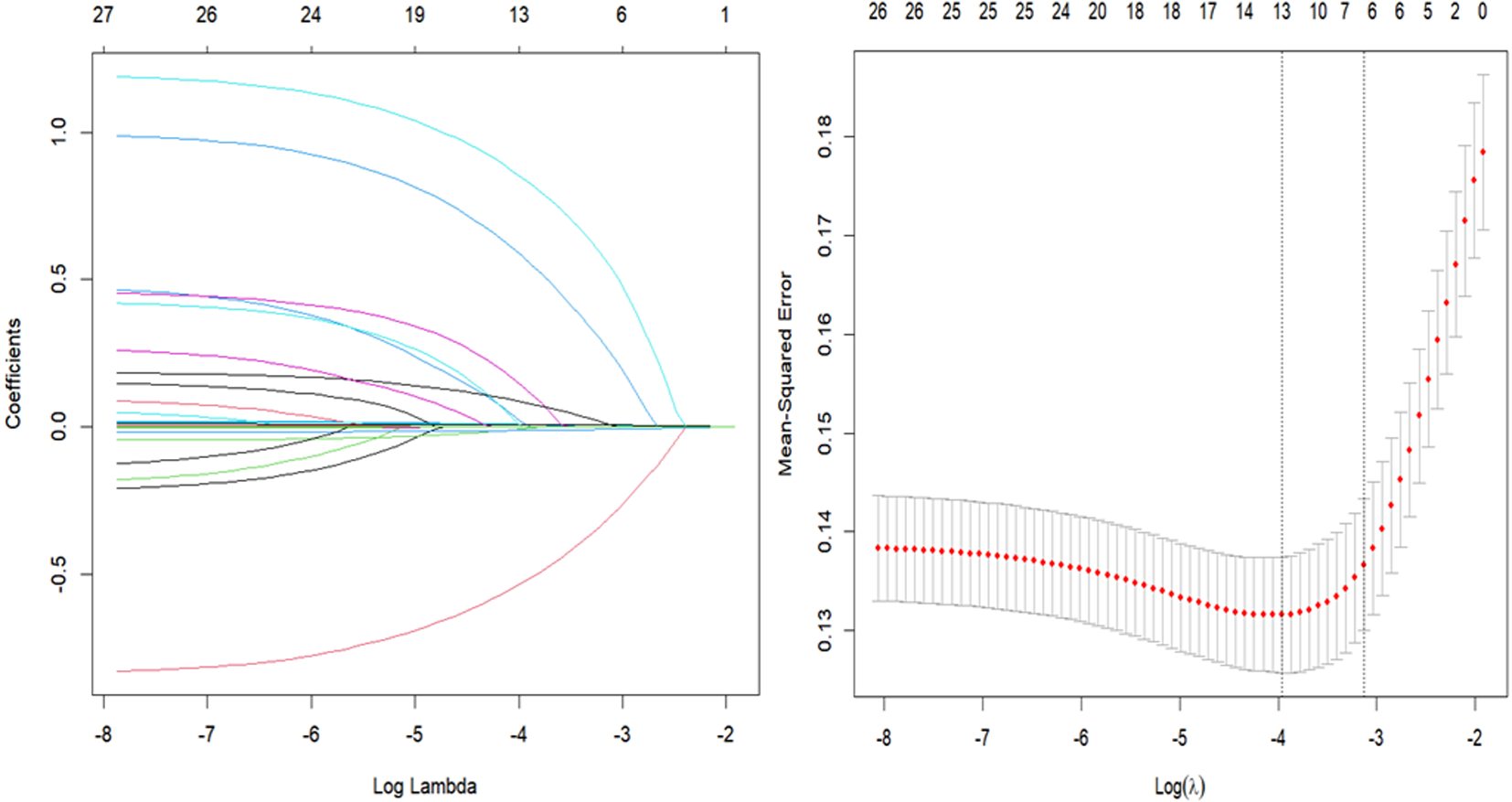
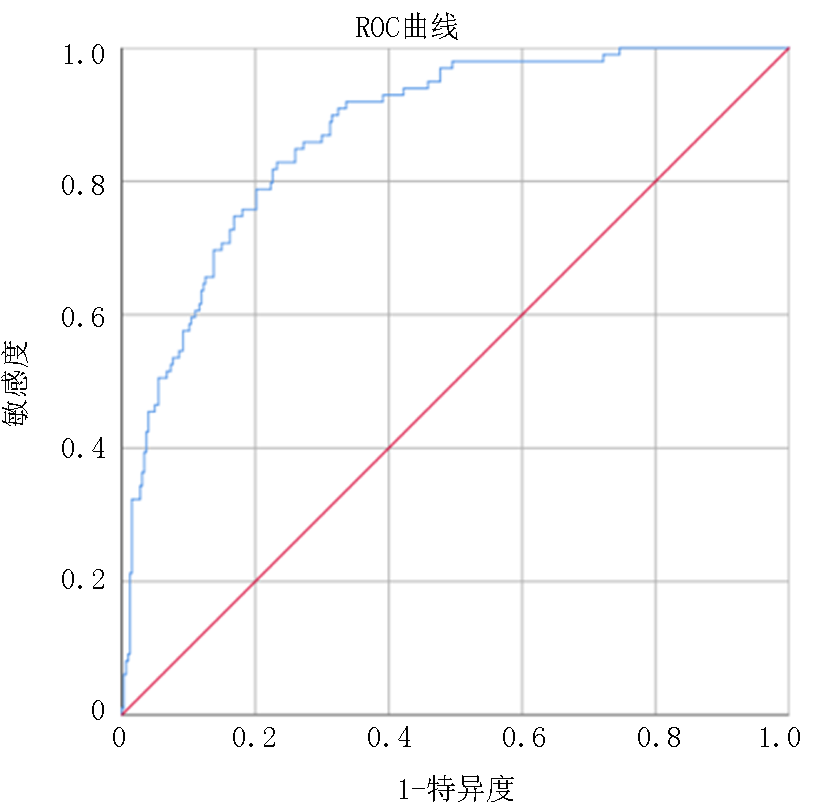
| [1] |
Binda F, Marelli F, Galazzi A, et al. Pressure ulcers after prone positioning in patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A cross-sectional study[J]. Nurs Crit Care, 2024, 29(1): 65-72.
|
| [2] |
Lin H, Chen H, Wang J, et al. Nomogram for intraoperatively acquired pressure injuries in children undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: A retrospective study[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2024, 24(1): 510.
doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04989-4
pmid: 39118018
|
| [3] |
樊小倩, 孙晴, 仲怀凤, 等. 体外循环心脏术后并发压力性损伤预测模型的建立[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2022, 47(12): 1752-1755.
|
| [4] |
Saleh MYN, Ibrahim EIM. Prevalence, severity, and characteristics of medical device related pressure injuries in adult intensive care patients: A prospective observational study[J]. Int Wound J, 2023, 20(1): 109-119.
|
| [5] |
Karacabay K, Savci A, Dalkılıç M, et al. Determining the incidence and risk factors of medical device-related pressure injury in intensive care patients[J]. J Tissue Viability, 2023, 32(4): 596-600.
|
| [6] |
美国欧洲压力性溃疡咨询委员会, 美国压力性损伤咨询委员会,美国泛太平洋压力性损伤联盟. 压力性损伤临床防治国际指南2019第3版[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2021.
|
| [7] |
杨茂凡, 周会兰, 陈柯宇, 等. ICU经口气管插管患者口腔黏膜压力性损伤研究进展[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(2): 21-24.
|
| [8] |
李茜, 王丽竹, 朱祎容, 等. ICU经口气管插管患者口腔黏膜压力性损伤的研究进展[J]. 中华急危重症护理杂志, 2023, 4(5): 473-477.
|
| [9] |
Govender K, Cabrales P. Extracorporeal circulation impairs microcirculation perfusion and organ function[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2022, 132(3): 794-810.
|
| [10] |
Chen G, Li X, Li X, et al. Mucosal membrane pressure injury in intensive care units: A scoping review[J]. Intensive Crit Care Nurs, 2024, 80:103560.
|
| [11] |
唐莉, 李敏, 姚倩. 经口气管插管病人口腔黏膜压力性损伤护理的研究进展[J]. 护理研究, 2023, 37(20): 3682-3686.
|
| [12] |
曲超然. 基于机器学习的心血管疾病患者术中压力性损伤预测模型构建[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021.
|
| [13] |
陈燕萍. 体外循环术后患者压力性损伤发生特征及影响因素分析[J]. 当代护士(中旬刊), 2019, 26(12): 158-161.
|
| [14] |
Wang Y, Liu B, Pi Y, et al. Risk factors for diabetic foot ulcers mortality and novel negative pressure combined with platelet-rich plasma therapy in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1051299.
|
| [15] |
Lyu Y, Huang YL, Li ZY, et al. Interventions and strategies to prevent medical device-related pressure injury in adult patients: A systematic review[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2023, 32(19-20): 6863-6878.
doi: 10.1111/jocn.16790
pmid: 37300246
|
| [16] |
王震, 张伟英. 小儿术中获得性压力性损伤影响因素分析及风险预测模型构建[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(13): 2292-2297.
|
| [17] |
Gou L, Zhang Z, AY. Risk factors for medical device-related pressure injury in ICU patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PloS One, 2023, 18(6): e0287326.
|
| [18] |
张诗怡, 赵体玉, 乐霄, 等. 术中压力性损伤与受压部位微环境关系的研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2021, 36(4): 40-42, 61.
|
| [19] |
王冰黎. 成人ICU患者器械相关压力性损伤风险预测模型构建及验证[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2023.
|
| [20] |
孙梅林, 李坤, 赵丽丽. 成人心血管手术患者压力性损伤发生现状调查及危险因素分析[J]. 齐鲁护理杂志, 2021, 27(2): 32-35.
|
| [21] |
Kimura N, Nakagami G, Minematsu T, et al. Non-invasive detection of local tissue responses to predict pressure ulcer development in mouse models[J]. J Tissue Viability, 2020, 29(1): 51-57.
doi: S0965-206X(19)30066-X
pmid: 31757582
|
| [22] |
Sun XX, Chen RB, Fang PP, et al. Model construction of factors influencing intensive care unit nurses' medical device-related pressure injury knowledge, attitude, and practice[J]. Int Wound J, 2023, 20(7): 2582-2593.
|
| [23] |
Strazzieri-Pulido KC, S González CV, Nogueira P, et al. Pressure injuries in critical patients: Incidence, patient-associated factors, and nursing workload[J]. J Nurs Manag, 2019, 27(2): 301-310.
|
 )
)