Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 222-226.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.03.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
A clinical investigation into the role of family members involved in the rehabilitation training for individuals with acute ischemic stroke
Bu Zhiping, ZhaoYu , Liu Hongfeng, Liu Guangliang, Han Wenqin( )
)
- Department of Neurology, Liangxiang Hospital of Beijing Fangshan District, Beijing 102401, China
-
Received:2024-12-24Online:2025-03-20Published:2025-03-25 -
Contact:Han Wenqin E-mail:rainbowhlh@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bu Zhiping, ZhaoYu , Liu Hongfeng, Liu Guangliang, Han Wenqin. A clinical investigation into the role of family members involved in the rehabilitation training for individuals with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(3): 222-226.
share this article
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(例) | 年龄 (岁) | 既往史[例(%)] | 吸烟史 [例(%)] | 阿替普酶溶栓 [例(%)] | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性 | 女性 | 高血压 | 心房颤动 | 糖尿病 | 冠心病 | 脑卒中 | ||||||||||||
| 治疗组 | 59 | 48 | 11 | 61(54,69.5) | 43(72.9) | 4(6.8) | 25(42.4) | 14(23.7) | 18(30.5) | 23(39.0) | 9(15.3) | |||||||
| 对照组 | 61 | 46 | 15 | 64(57,69.5) | 45(73.8) | 4(6.6) | 30(49.2) | 8(13.1) | 18(29.5) | 23(37.7) | 12(19.7) | |||||||
| Z/χ2值 | 0.625 | 1.340 | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.560 | 2.257 | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.405 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.429 | 0.183 | 0.912 | 1.000 | 0.454 | 0.133 | 0.905 | 0.886 | 0.524 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 入院时收缩压 (mmHg) | 入院时NIHSS 评分(分) | 入组距发病 时间(d) | 入组时FuglMeyer 评分(分) | 入组时Barthel 评分(分) | 入组时焦虑自评 量表评分(分) | 入组时抑郁量表 自测评分(分) | |||||||||||
| 治疗组 | 149(135,167) | 5(1,16) | 6(3,10) | 64(55,76) | 60(50,75) | 35(30,37) | 30(28,34) | |||||||||||
| 对照组 | 152(134.5,166.5) | 5(1,16) | 5(3,10) | 70(62,80) | 60(45,70) | 34(32,36) | 33(29,34) | |||||||||||
| Z值 | 0.776 | 0.660 | 0.410 | 1.308 | 0.604 | 0.081 | 1.799 | |||||||||||
| P值 | 0.439 | 0.511 | 0.682 | 0.301 | 0.547 | 0.935 | 0.075 | |||||||||||
Tab.1 Baseline characteristics between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(例) | 年龄 (岁) | 既往史[例(%)] | 吸烟史 [例(%)] | 阿替普酶溶栓 [例(%)] | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性 | 女性 | 高血压 | 心房颤动 | 糖尿病 | 冠心病 | 脑卒中 | ||||||||||||
| 治疗组 | 59 | 48 | 11 | 61(54,69.5) | 43(72.9) | 4(6.8) | 25(42.4) | 14(23.7) | 18(30.5) | 23(39.0) | 9(15.3) | |||||||
| 对照组 | 61 | 46 | 15 | 64(57,69.5) | 45(73.8) | 4(6.6) | 30(49.2) | 8(13.1) | 18(29.5) | 23(37.7) | 12(19.7) | |||||||
| Z/χ2值 | 0.625 | 1.340 | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.560 | 2.257 | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.405 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.429 | 0.183 | 0.912 | 1.000 | 0.454 | 0.133 | 0.905 | 0.886 | 0.524 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 入院时收缩压 (mmHg) | 入院时NIHSS 评分(分) | 入组距发病 时间(d) | 入组时FuglMeyer 评分(分) | 入组时Barthel 评分(分) | 入组时焦虑自评 量表评分(分) | 入组时抑郁量表 自测评分(分) | |||||||||||
| 治疗组 | 149(135,167) | 5(1,16) | 6(3,10) | 64(55,76) | 60(50,75) | 35(30,37) | 30(28,34) | |||||||||||
| 对照组 | 152(134.5,166.5) | 5(1,16) | 5(3,10) | 70(62,80) | 60(45,70) | 34(32,36) | 33(29,34) | |||||||||||
| Z值 | 0.776 | 0.660 | 0.410 | 1.308 | 0.604 | 0.081 | 1.799 | |||||||||||
| P值 | 0.439 | 0.511 | 0.682 | 0.301 | 0.547 | 0.935 | 0.075 | |||||||||||
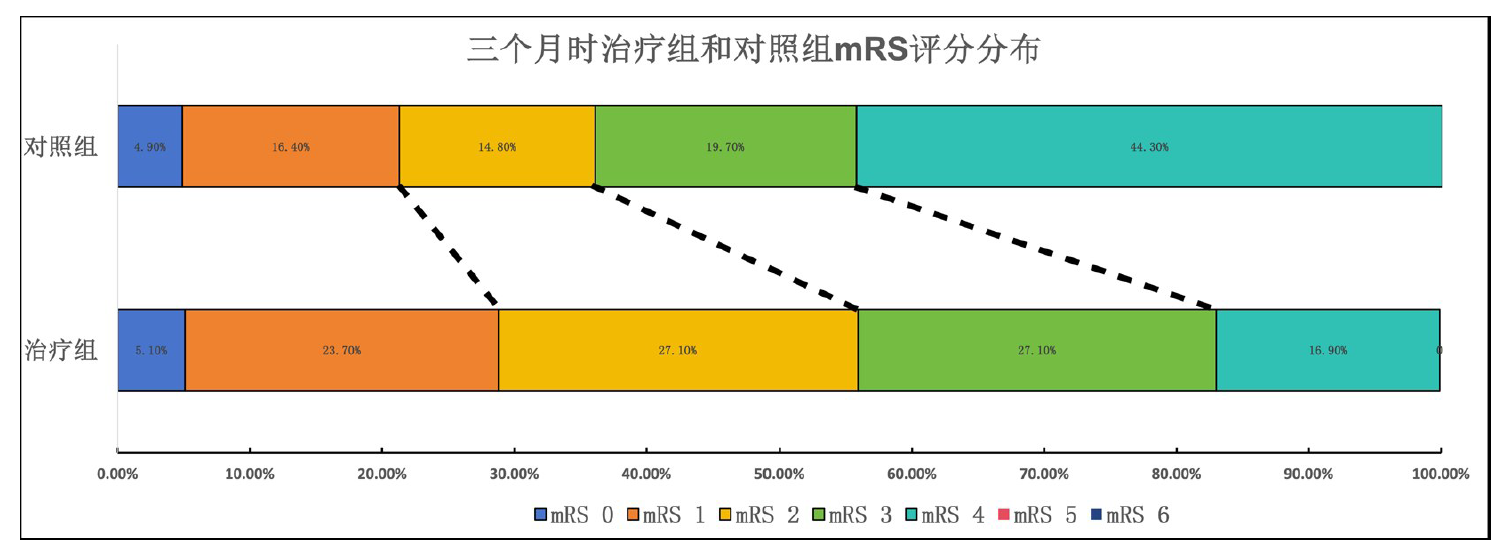
| 组别 | 例数 | 90 d mRS 0~1 | 90 d mRS 0~2 | 90 d mRS 0~3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗组 | 59 | 17(28.8) | 33(55.9) | 49(83.1) |
| 对照组 | 61 | 13(21.3) | 22(36.1) | 34(55.7) |
| χ2值 | 0.946 | 2.168 | 3.143 | |
| OR及95%置信区间 | 1.5(0.65~3.44) | 2.25(1.08~4.68) | 3.89(1.66~9.07) | |
| P值 | 0.344 | 0.030 | 0.002 |
Tab.2 The 90-day mRS scores between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 90 d mRS 0~1 | 90 d mRS 0~2 | 90 d mRS 0~3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗组 | 59 | 17(28.8) | 33(55.9) | 49(83.1) |
| 对照组 | 61 | 13(21.3) | 22(36.1) | 34(55.7) |
| χ2值 | 0.946 | 2.168 | 3.143 | |
| OR及95%置信区间 | 1.5(0.65~3.44) | 2.25(1.08~4.68) | 3.89(1.66~9.07) | |
| P值 | 0.344 | 0.030 | 0.002 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 90 d FuglMeyer 评分增加 | 90 d Barthel 评分改善 | 90 d焦虑自评 量表评分下降 | 90 d抑郁自评 量表分下降 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗组 | 59 | 18(10,24) | 25(15,30) | 9(2,15) | 4(0,5) |
| 对照组 | 61 | 12(8,20.5) | 20(15,31) | 7(0,10.5) | 2(0,6) |
| Z值 | 2.101 | 2.023 | 1.739 | 2.030 | |
| P值 | 0.038 | 0.045 | 0.085 | 0.045 |
Tab.3 The improvements in 90-day FMS, Barthel index, anxiety, and depression scores between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 90 d FuglMeyer 评分增加 | 90 d Barthel 评分改善 | 90 d焦虑自评 量表评分下降 | 90 d抑郁自评 量表分下降 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗组 | 59 | 18(10,24) | 25(15,30) | 9(2,15) | 4(0,5) |
| 对照组 | 61 | 12(8,20.5) | 20(15,31) | 7(0,10.5) | 2(0,6) |
| Z值 | 2.101 | 2.023 | 1.739 | 2.030 | |
| P值 | 0.038 | 0.045 | 0.085 | 0.045 |
| [1] | 《中国脑卒中防治报告2021》编写组,王陇德. 《中国脑卒中防治报告2021》概要[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2023, 20(11):783-792. |
| [2] |
Langhorne P, Wu O, Rodgers H, et al. A very early rehabilitation trial after stroke (AVERT): A phase III, multicentre, randomised controlled trial[J]. Health Technol Assess, 2017, 21(54):1-120.
doi: 10.3310/hta21540 pmid: 28967376 |
| [3] | 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性卒中诊治指南2023[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2024, 57(6):523-559. |
| [4] | Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association[J]. Stroke, 2019, 50(12):e344-e418. |
| [5] | 孟祥红, 王文志, 戴红, 等. 北京市崇文区脑卒中康复现状调查分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2009, 24(3):255-258. |
| [6] | 吴艳琳, 朱强, 张家红, 等. 脑卒中患者家庭远程康复的研究进展[J]. 中国医药导报, 2023, 20(23):56-59. |
| [7] | 闫玮娟, 刘杰, 梁涛, 等. 团体治疗对卒中后抑郁患者日常生活能力的影响[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2015, (3):402-404. |
| [8] |
Kootker JA, Rasquin SM, Smits P, et al. An augmented cognitive behavioural therapy for treating post-stroke depression: Description of a treatment protocol[J]. Clin Rehabil, 2015, 29(9):833-843.
doi: 10.1177/0269215514559987 pmid: 25452633 |
| [9] |
Finkenzeller W, Zobel I, Rietz S, et al. Interpersonal psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for post-stroke depression. Feasibility and effectiveness[J]. Nervenarzt, 2009, 80(7):805-812.
doi: 10.1007/s00115-008-2649-1 pmid: 19455296 |
| [10] |
Briggs DE, Felberg RA, Malkoff MD, et al. Should mild or moderate stroke patients be admitted to an intensive care unit?[J]. Stroke, 2001, 32(4):871-876.
pmid: 11283385 |
| [11] | 刘松怀, 梁志锋, 洪晔, 等. 不同心理阶段康复患者心理治疗策略探讨[J]. 第五届北京国际康复论坛论文集, 2010, 743-748. |
| [12] |
Tong Y, Cheng Z, Rajah GB, et al. High intensity physical rehabilitation later than 24 h post stroke is beneficial in patients: A pilot randomized controlled trial (RCT) study in mild to moderate ischemic stroke[J]. Front Neurol, 2019, 10:113.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00113 pmid: 30837938 |
| [13] | 赵丽华, 王爱林, 徐珍凤. 脑卒中患者家庭康复锻炼依从性现状及影响因素调查分析[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2020, 33(18):3110-3112. |
| [14] | 韩通, 胡川, 刘宝祥, 等. 基于互联网模式下的脑卒中延续家庭康复疗效观察[J]. 中国康复, 2022, 37(9):546-548. |
| [15] |
Teasell R, Salbach NM, Foley N, et al. Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: Rehabilitation, recovery, and community participation following stroke. Part one: Rehabilitation and recovery following stroke; 6th edition update 2019[J]. Int J Stroke, 2020, 15(7):763-788.
doi: 10.1177/1747493019897843 pmid: 31983296 |
| [16] |
Rochette A, Racine E, Lefebvre H, et al. Ethical issues relating to the inclusion of relatives as clients in the post-stroke rehabilitation process as perceived by patients, relatives and health professionals[J]. Patient Educ Couns, 2014, 94(3):384-389.
doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2013.10.028 pmid: 24290239 |
| [17] | 王冉, 张英, 陈芳婷, 等. 家庭远程康复对脑卒中恢复后期患者运动功能和日常生活活动能力的影响[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2020, 41(5):815-818. |
| [18] | 舒小珉, 化艳, 张维珍. 以家庭为中心的护理模式在中风偏瘫病人康复训练中的应用[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(5):886-888. |
| [19] | 张亚静, 刘昱宏, 许美丽. 基于家庭赋权的护理干预结合感觉运动训练对脑卒中恢复期患者肢体功能及康复锻炼积极性的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2024, 9(9):149-152. |
| [20] | 叶海程, 甘卫冬. 家庭-住院循环卒中康复模式对脑卒中患者功能恢复的影响及卫生经济学评价[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2024, 39(12):1886-1889. |
| [21] |
戴剑, 王丽清, 程家欣, 等. 心理康复在卒中后抑郁治疗中的研究进展[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2024, 41(3):241-245.
doi: 10.19845/j.cnki.zfysjjbzz.2024.0047 |
| [22] | 陈蕾, 黄雪薇. 心理治疗的生理机制[J]. 医学信息(下旬刊), 2013, 26(15):574. |
| [23] |
Thomas SA, Drummond AE, Lincoln NB, et al. Behavioural activation therapy for post-stroke depression: The BEADS feasibility RCT[J]. Health Technol Assess, 2019, 23(47):1-176.
doi: 10.3310/hta23470 pmid: 31524133 |
| [24] | 时红梅, 李依芃, 靳智凯, 等. 心理支持配合早期康复干预对缺血性脑卒中患者康复的效果评价[J]. 中国康复, 2020, 35(1):12-14. |
| [25] | 侯慧卿, 王晓曦, 李沙, 等. 家庭功能与社会支持对中年脑卒中后抑郁的影响[J]. 河北医药, 2021, 43(9):1326-1329, 1334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||