Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 349-354.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.04.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical analysis of nine cases with positive transcranial Doppler ultrasound neck rotation test and literature review
Jia Yanqiu, Huo Tiantian, Fan Mingyue, He Shasha, Jin Wei, Lyu Peiyuan( )
)
- Department of Neurology,Hebei General Hospital /Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Cerebral Networks and Cognitive Disorders,Shijiazhuang 050051,China
-
Received:2025-02-12Online:2025-04-20Published:2025-04-17 -
Contact:Lyu Peiyuan E-mail:peiyuanlu2@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jia Yanqiu, Huo Tiantian, Fan Mingyue, He Shasha, Jin Wei, Lyu Peiyuan. Clinical analysis of nine cases with positive transcranial Doppler ultrasound neck rotation test and literature review[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(4): 349-354.
share this article
| 例序 | 性别 | 年龄 (岁) | 病例 来源 | 主诉 | 颈部血管 超声 | MRA | 累及动脉 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 女 | 44 | 门诊 | 间断头晕1周,以转头时明显 | 未见异常 | - | R/LVA |
| 2 | 男 | 34 | 门诊 | 间断头晕1月,与头部活动有关 | - | - | R/LVA |
| 3 | 女 | 58 | 门诊 | 发作性头晕2月余,与头部活动有关 | RVA纤细 | BA起源于LICA | LVA |
| 4 | 男 | 46 | 住院 | 头部活动时头晕1月余 | 未见异常 | RVA纤细,未汇入BA | LVA |
| 5 | 女 | 59 | 门诊 | 头晕20余天,与头部活动有关 | - | - | LVA |
| 6 | 男 | 41 | 门诊 | 头晕恶心10余天,与头部活动有关 | - | - | LVA |
| 7 | 女 | 60 | 住院 | 头晕耳鸣20余天,头晕似乎与头部活动相关 | 未见异常 | 未见异常 | RVA |
| 8 | 男 | 22 | 门诊 | 间断头晕4年,向右侧转头时明显 | - | RVA纤细,颅内段未见明确显示 | LVA |
| 9 | 男 | 30 | 门诊 | 转头时头晕1年,加重1周 | - | - | RVA |
Tab. 1 Clinical data of nine patients with positive TCD neck rotation test
| 例序 | 性别 | 年龄 (岁) | 病例 来源 | 主诉 | 颈部血管 超声 | MRA | 累及动脉 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 女 | 44 | 门诊 | 间断头晕1周,以转头时明显 | 未见异常 | - | R/LVA |
| 2 | 男 | 34 | 门诊 | 间断头晕1月,与头部活动有关 | - | - | R/LVA |
| 3 | 女 | 58 | 门诊 | 发作性头晕2月余,与头部活动有关 | RVA纤细 | BA起源于LICA | LVA |
| 4 | 男 | 46 | 住院 | 头部活动时头晕1月余 | 未见异常 | RVA纤细,未汇入BA | LVA |
| 5 | 女 | 59 | 门诊 | 头晕20余天,与头部活动有关 | - | - | LVA |
| 6 | 男 | 41 | 门诊 | 头晕恶心10余天,与头部活动有关 | - | - | LVA |
| 7 | 女 | 60 | 住院 | 头晕耳鸣20余天,头晕似乎与头部活动相关 | 未见异常 | 未见异常 | RVA |
| 8 | 男 | 22 | 门诊 | 间断头晕4年,向右侧转头时明显 | - | RVA纤细,颅内段未见明确显示 | LVA |
| 9 | 男 | 30 | 门诊 | 转头时头晕1年,加重1周 | - | - | RVA |
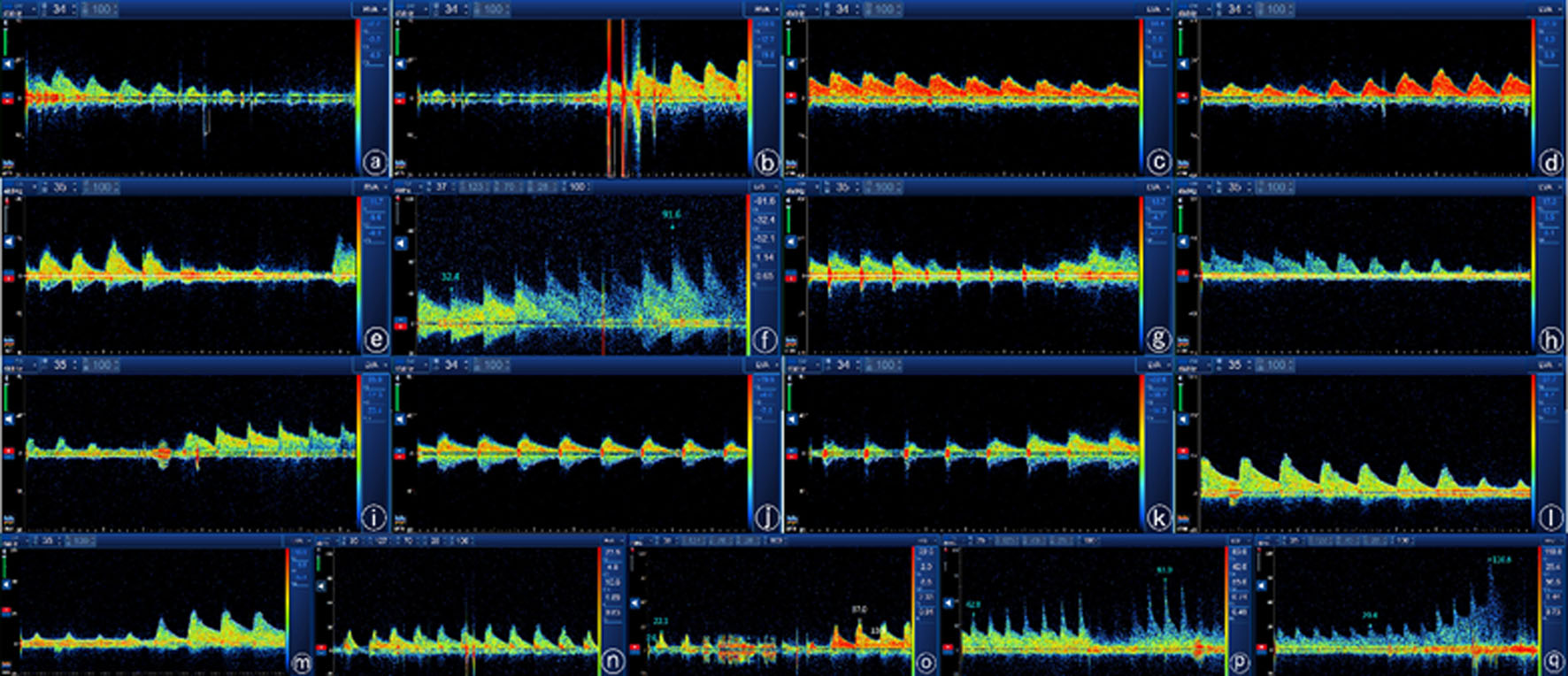
Fig. 1 VA spectra of nine patients with positive TCD neck rotation test a. Case 1: Turning the neck to the left side, RVA3 blood flow velocity decreased to baseline; c. Case 1: Turning the neck to the right, the LVA3 blood flow velocity decreased significantly; e. Case 2: Turning the neck to the left, RVA3 blood flow velocity decreased to baseline; f. Case 2: Turning the neck to the right, the LVA3 blood velocity was significantly elevated; g. Case 3: Turning the neck to the right side, the LVA3 blood flow velocity was significantly reduced; h. Case 4: Turning the neck to the right side, LVA3 blood flow velocity decreased to baseline; j. Case 5: Turning the neck to the right side, LVA3 blood flow velocity was significantly reduced; l. Case 6: Turning the neck to the right side, LVA3 blood flow velocity was significantly reduced; n. Case 7: Turning the neck to the left side, RVA3 blood flow velocity was significantly reduced; p. Case 8: Turning the neck to the right side, the LVA3 blood flow rate was significantly elevated; q. Case 9: Turning the neck to the left side, the RVA3 blood flow rate was significantly elevated; b, d, e, g, i, k, m, o. Blood flow resumed after postural recovery.
| 例序 | LVA3转颈试验向右(cm/s) | RVA3转颈试验向左(cm/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30→10 | 34→0 |
| 2 | 32→91 | 46→0 |
| 3 | 29→5 | 10,探查欠满意 |
| 4 | 44→0 | 16,转颈无变化 |
| 5 | 22→10 | 53,转颈无变化 |
| 6 | 45→11 | 41,转颈无变化 |
| 7 | 40,转颈无变化 | 37→8 |
| 8 | 42→83 | 探查不满意 |
| 9 | 34,转颈无变化 | 29→110 |
Tab. 2 TCD neck rotation test blood flow velocity in nine patients
| 例序 | LVA3转颈试验向右(cm/s) | RVA3转颈试验向左(cm/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30→10 | 34→0 |
| 2 | 32→91 | 46→0 |
| 3 | 29→5 | 10,探查欠满意 |
| 4 | 44→0 | 16,转颈无变化 |
| 5 | 22→10 | 53,转颈无变化 |
| 6 | 45→11 | 41,转颈无变化 |
| 7 | 40,转颈无变化 | 37→8 |
| 8 | 42→83 | 探查不满意 |
| 9 | 34,转颈无变化 | 29→110 |
| [1] |
Sorensen BF. Bow hunter's stroke[J]. Neurosurgery, 1978, 2(3):259-261.
doi: 10.1227/00006123-197805000-00013 pmid: 732978 |
| [2] | Ndongo Sonfack DJ, Bojanowski MW, Tarabay B, et al. Vertebral artery stenosis from osteophyte: A systematic review and case series[J]. Neurochirurgie, 2024, 70(3):101525. |
| [3] |
Cornelius JF, Slotty PJ, Tortora A, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome caused by compression of the subaxial vertebral artery: Surgical technique of anterolateral decompression (video)[J]. World Neurosurg, 2018, 119:358-361.
doi: S1878-8750(18)31905-3 pmid: 30165215 |
| [4] |
Ng S, Boetto J, Favier V, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome: Surgical vertebral artery decompression guided by dynamic intraoperative angiography[J]. World Neurosurg, 2018, 118:290-295.
doi: S1878-8750(18)31630-9 pmid: 30059781 |
| [5] |
Cai DZ, Roach RP, Weaver JP, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome in a patient with a right hypoplastic vertebral artery and a dynamically compressible left vertebral artery[J]. Asian J Neurosurg, 2018, 13(1):133-135.
doi: 10.4103/1793-5482.181129 pmid: 29492144 |
| [6] | Simpkin CT, Davis KE, Davis BS, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome in a patient with vertebral artery atresia, an arcuate foramen, and unilateral deafness: A case report[J]. Radiol Case Rep, 2017, 12(3):597-601. |
| [7] |
Lukianchikov V, Lvov I, Grin A, et al. Minimally invasive surgical treatment for vertebral artery compression in a patient with one-sided ponticulus posticus and ponticulus lateralis[J]. World Neurosurg, 2018, 117:97-102.
doi: S1878-8750(18)31216-6 pmid: 29902609 |
| [8] | Jadeja N, Nalleballe K. Pearls & Oy-sters: Bow hunter syndrome: A rare cause of posterior circulation stroke: Do not look the other way[J]. Neurology, 2018, 91(7):329-331. |
| [9] |
Sakamoto Y, Kimura K, Iguchi Y, et al. An embolic bow hunter's stroke associated with anomaly of cervical spine[J]. Neurology, 2011, 77(14):1403-1404.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31823152f9 pmid: 21968846 |
| [10] |
Fujii M, Ohgushi M, Chin T. Brain infarction due to vertebral artery dissection caused by a bone protrusion from the condylar fossa in a juvenile case[J]. Br J Neurosurg, 2020, 34(2):232-234.
doi: 10.1080/02688697.2018.1435850 pmid: 29405773 |
| [11] | Yang H, Zhong S, Hu Y, et al. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion in a patient with basilar invagination[J]. Br J Neurosurg, 2023, 37(4):650-652. |
| [12] | Eghbal K, Derakhshan N, Haghighat A. Ocular manifestation of a cervical spine injury: An adult case of traumatic atlantoaxial rotatory subluxation manifesting with nystagmus[J]. World Neurosurg, 2017, 101:811-817. |
| [13] |
Saito K, Hirano M, Taoka T, et al. Artery-to-artery embolism with a mobile mural thrombus due to rotational vertebral artery occlusion[J]. J Neuroimaging, 2010, 20(3):284-286.
doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6569.2008.00309.x pmid: 19021833 |
| [14] |
Cornelius JF, Slotty P, El KM, et al. Hemodynamic stroke: A rare pitfall in cranio cervical junction surgery[J]. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine, 2014, 5(3):122-124.
doi: 10.4103/0974-8237.142306 pmid: 25336834 |
| [15] | Missori P, Marruzzo D, Peschillo S, et al. Clinical remarks on acute post-traumatic atlanto-axial rotatory subluxation in pediatric-aged patients[J]. World Neurosurg, 2014, 82(5):e645-e648. |
| [16] | Eura N, Saito K, Shimizu H, et al. A thromboembolic mechanism in bow hunter's stroke: Importance of hemodynamic evaluation by ultrasonography during head rotation[J]. eNeurologicalSci, 2020, 20:100254. |
| [17] | Patankar AP. Vertebro-basilar stroke due to bow-hunter syndrome: An unusual presentation of rotatory atlanto-axial subluxation in a fourteen year old[J]. Br J Neurosurg, 2023, 37(4):808-810. |
| [18] | Pinol I, Ramirez M, Salo G, et al. Symptomatic vertebral artery stenosis secondary to cervical spondylolisthesis[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2013, 38(23):e1503-e1505. |
| [19] | Wong SC, Chan TS, Chan CH, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome: A sinister cause of vertigo and syncope not to be missed[J]. Hong Kong Med J, 2020, 26(2):150-151. |
| [20] | Jost GF, Dailey AT. Bow hunter's syndrome revisited: 2 New cases and literature review of 124 cases[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2015, 38(4):e7. |
| [21] | Wang S, Bi Y, Chen Y. Bilateral bow hunter syndrome associated with loss of cervical physiological curvature[J]. Am J Case Rep, 2024, 25: e942609. |
| [22] |
Yamaguchi S, Horie N, Tsunoda K, et al. Bow hunter's stroke due to stretching of the vertebral artery fenestration: A case report[J]. NMC Case Rep J, 2015, 2(1):9-11.
doi: 10.2176/nmccrj.2014-0075 pmid: 28663954 |
| [23] | Motiei-Langroudi R, Griessenauer CJ, Alturki A, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome from a tortuous v1 segment vertebral artery treated with stent placement[J]. World Neurosurg, 2017, 98:811-878. |
| [24] | Johnson SA, Ducruet AF, Bellotte JB, et al. Rotational vertebral artery dissection secondary to anomalous entrance into transverse foramen[J]. World Neurosurg, 2017, 108:991-998. |
| [25] | Shimizu S, Yamada M, Takagi H, et al. Bow hunter's stroke associated with an aberrant course of the vertebral artery--case report[J]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo), 1999, 39(12):867-869. |
| [26] |
Rendon R, Mannoia K, Reiman S, et al. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion secondary to completely extraosseous vertebral artery[J]. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech, 2019, 5(1):14-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2018.09.006 pmid: 30619984 |
| [27] | Buch VP, Madsen PJ, Vaughan KA, et al. Rotational vertebrobasilar insufficiency due to compression of a persistent first intersegmental vertebral artery variant: Case report[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2017, 26(2):199-202. |
| [28] |
Dabus G, Gerstle RJ, Parsons M, et al. Rotational vertebrobasilar insufficiency due to dynamic compression of the dominant vertebral artery by the thyroid cartilage and occlusion of the contralateral vertebral artery at C1-2 level[J]. J Neuroimaging, 2008, 18(2):184-187.
doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6569.2007.00177.x pmid: 18298678 |
| [29] |
Sell JJ, Rael JR, Orrison WW. Rotational vertebrobasilar insufficiency as a component of thoracic outlet syndrome resulting in transient blindness. Case report[J]. J Neurosurg, 1994, 81(4):617-619.
pmid: 7931599 |
| [30] | Sarkar J, Wolfe SQ, Ching BH, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome causing vertebrobasilar insufficiency in a young man with neck muscle hypertrophy[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2014, 28(4):1031-1032. |
| [31] |
Dadsetan MR, Skerhut HE. Rotational vertebrobasilar insufficiency secondary to vertebral artery occlusion from fibrous band of the longus coli muscle[J]. Neuroradiology, 1990, 32(6):514-515.
pmid: 2287384 |
| [32] |
Karabacak M, Ozkara BB, Ozaydin B, et al. What you need to know about: Arterial cerebrovascular syndromes caused by static or dynamic musculoskeletal compression[J]. Br J Hosp Med (Lond), 2022, 83(3):1-9.
doi: 10.12968/hmed.2021.0091 pmid: 35377211 |
| [33] |
Mori M, Yamahata H, Yamaguchi S, et al. Bow-hunter's syndrome due to left C7 schwannoma in a patient with bilateral absence of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery[J]. J Orthop Sci, 2019, 24(5):939-944.
doi: S0949-2658(17)30087-8 pmid: 28456352 |
| [34] |
Haimoto S, Nishimura Y, Hara M, et al. Surgical treatment of rotational vertebral artery syndrome induced by spinal tumor: A case report and literature review[J]. NMC Case Rep J, 2017, 4(4):101-105.
doi: 10.2176/nmccrj.cr.2016-0152 pmid: 29018650 |
| [35] |
Akar Z, Kafadar AM, Tanriover N, et al. Rotational compression of the vertebral artery at the point of dural penetration. Case report[J]. J Neurosurg, 2000, 93(2 Suppl):300-303.
pmid: 11012064 |
| [36] | Kitahara H, Takeda T, Akasaka K, et al. Bow hunter syndrome elicited by vertebral arterial occlusion after total arch replacement[J]. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg, 2017, 24(5):806-808. |
| [37] | Dohzono S, Sasaoka R, Takamatsu K, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome after cervical laminoplasty in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis with bony ankylosis in the cervical spine: A case report[J]. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep, 2020, 4(1):11-15. |
| [38] | Kan P, Srivatsan A, Johnnson JN, et al. Rotational carotid insufficiency: An unusual cause of bow hunter's syndrome[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2018, 2018. |
| [39] | Brinjikji W, Graffeo CS, Perry A, et al. Moving target: Transient rotational stenosis precipitating jugular bow hunter's syndrome[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2017, 9(7):e28. |
| [40] | Santirso D, Garami Z, Diaz O, et al. Ultrasound during neck rotation to reveal a case of positional occlusion of the internal carotid artery[J]. J Ultrasound, 2022, 25(2):297-300. |
| [41] | Enomoto N, Yagi K, Matsubara S, et al. Case report: Bow hunter's syndrome caused by compression of extracranially originated posterior inferior cerebellar artery[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12:756838. |
| [42] |
Tokashiki N, Ikenouchi H, Miyamoto T, et al. Occult bow hunter's syndrome as a hidden cause of recurrent posterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction[J]. Acta Neurol Belg, 2023, 123(3):1169-1171.
doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02227-9 pmid: 36854934 |
| [43] |
Cornelius JF, George B, N'Dri OD, et al. Bow-hunter's syndrome caused by dynamic vertebral artery stenosis at the cranio-cervical junction--a management algorithm based on a systematic review and a clinical series[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2012, 35(1):127-135, 135.
doi: 10.1007/s10143-011-0343-4 pmid: 21789571 |
| [44] | Kuether TA, Nesbit GM, Clark WM, et al. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion: A mechanism of vertebrobasilar insufficiency[J]. Neurosurgery, 1997, 41(2):427-432,432-433. |
| [45] | Lee CS, Lee HY, Yang TK. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion syndrome: Misnomers and classification[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2015, 131:18-20. |
| [46] | Shi C, Wang L, Dou Y, et al. Dynamic CT angiography of the head and neck in the diagnosis of bow hunter's syndrome: A case report[J]. Radiol Case Rep, 2020, 15(11):2275-2277. |
| [47] |
Kimihira L, Yoshimoto T, Ihara M. New diagnostic algorithm for detection of covert bow hunter's syndrome[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2021, 18(10):2162-2165.
doi: 10.7150/ijms.56442 pmid: 33859523 |
| [48] | Takafumi S, Hojo R, Tsuchiyama T, et al. A case report of bow hunter's syndrome with intravascular ultrasound showing changing significant severe stenosis of the left vertebral artery associated with turning left[J]. Eur Heart J Case Rep, 2024, 8(1):ytad639. |
| [49] |
Velat GJ, Reavey-Cantwell JF, Ulm AJ, et al. Intraoperative dynamic angiography to detect resolution of bow hunter's syndrome: Technical case report[J]. Surg Neurol, 2006, 66(4):420-423, 423.
pmid: 17015129 |
| [50] |
Nomura Y, Toi T, Ogawa Y, et al. Transitional nystagmus in a bow hunter's syndrome case report[J]. BMC Neurol, 2020, 20(1):435.
doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-02009-3 pmid: 33256636 |
| [51] | Schubert MC, Carter N, Lo SL. Case report: Bow hunter syndrome-one reason to add non-gravity dependent positional nystagmus testing to your clinical neuro-otologic exam[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12:814998. |
| [52] | Xue S, Shi H, Du X, et al. Bow hunter's syndrome combined with ipsilateral vertebral artery dissection/pseudoaneurysm: Case study and literature review[J]. Br J Neurosurg, 2023, 37(4):911-915. |
| [1] | Yang Fei;Zhu Xiaolong;Chen Jing;Zhu Yuexiang;Cui Shujun. Application of CT plain scan and multi-slice spiral CT angiography in diagnosis of vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia in elderly [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(3): 301-303304. |
| [2] | GUO Ming-sheng;LI Wei. Clinical characteristics of vertebral basilar artery system transient ischemic attack in winter and summer [J]. Clinical Focus, 2014, 29(12): 1342-1344. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||