Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 153-157.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.02.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of a prediction model for refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children based on lung ultrasound score
Li Dengfeng1, Huang Jiahu2, Li Tingjun2, Lv Yong3, Jin Zhenzhen3, Lian Shaofeng1( )
)
- 1. Department of Pediatrics, Jieshou People's Hospital, Jieshou 236500, China
2. Department of Emergency, Shanghai Children's Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200062, China
3. Department of Pediatrics, the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China (Anhui Provincial Hospital), Hefei 230001, China
-
Received:2024-11-01Online:2025-02-20Published:2025-03-05 -
Contact:Lian Shaofeng E-mail:Jseklsf@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Dengfeng, Huang Jiahu, Li Tingjun, Lv Yong, Jin Zhenzhen, Lian Shaofeng. Construction of a prediction model for refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children based on lung ultrasound score[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 153-157.
share this article
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄(月) | 热峰(℃) | 发热持续时间(h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | |||||
| n-RMPP | 378 | 197(22.5) | 181(20.7) | 59.5(40.0, 84.0) | 39.0(38.7, 39.4) | 96.0(40.5, 144.0) |
| RMPP | 498 | 249(28.5) | 248(28.3) | 58.0(38.0, 83.0) | 39.0(38.7, 39.4) | 144.0(120.0, 168.0) |
| χ2/Z值 | 0.349 | -0.448 | -1.002 | -10.573 | ||
| P值 | 0.555 | 0.654 | 0.316 | <0.001 | ||
Tab.1 Comparison of basic data between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄(月) | 热峰(℃) | 发热持续时间(h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | |||||
| n-RMPP | 378 | 197(22.5) | 181(20.7) | 59.5(40.0, 84.0) | 39.0(38.7, 39.4) | 96.0(40.5, 144.0) |
| RMPP | 498 | 249(28.5) | 248(28.3) | 58.0(38.0, 83.0) | 39.0(38.7, 39.4) | 144.0(120.0, 168.0) |
| χ2/Z值 | 0.349 | -0.448 | -1.002 | -10.573 | ||
| P值 | 0.555 | 0.654 | 0.316 | <0.001 | ||
| 组别 | 例数 | LUS(分) | WBC (×109/L) | 中性粒细胞计数 (×109/L) | 中性粒细胞百分比 (%) | NLR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-RMPP | 378 | 20(18, 23) | 7.87(7.26, 8.43) | 5.54(4.62, 6.15) | 71.2(64.8, 76.4) | 2.47(1.84, 3.24) | ||||||
| RMPP | 498 | 24(22, 27) | 7.48(6.30, 8.40) | 5.06(4.14, 6.05) | 68.9(63.7, 75.9) | 2.22(1.75, 3.14) | ||||||
| χ2/Z值 | -14.641 | -3.244 | -3.506 | -1.973 | -1.973 | |||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.048 | 0.048 | |||||||
| 组别 | CRP (mg/L) | PCT (μg/L) | SF (μg/L) | ESR (mm/h) | D-D (mg/L) | LDH (U/L) | ||||||
| n-RMPP | 6.0(5.0, 10.0) | 0.08(0.04, 0.23) | 28.15(14.15, 84.28) | 19.0(8.0, 37.0) | 0.38(0.23, 0.60) | 271.5(201.8, 334.0) | ||||||
| RMPP | 17.0(12.0, 23.0) | 0.60(0.08, 0.86) | 70.50(38.38, 124.38) | 20.0(7.8, 37.0) | 1.15(0.65, 2.51) | 515.0(406.0, 598.0) | ||||||
| χ2/Z值 | -16.451 | -10.117 | -9.527 | -0.229 | -16.447 | -21.048 | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.819 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
Tab. 2 Comparison of LUS and inflammatory indicators between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | LUS(分) | WBC (×109/L) | 中性粒细胞计数 (×109/L) | 中性粒细胞百分比 (%) | NLR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-RMPP | 378 | 20(18, 23) | 7.87(7.26, 8.43) | 5.54(4.62, 6.15) | 71.2(64.8, 76.4) | 2.47(1.84, 3.24) | ||||||
| RMPP | 498 | 24(22, 27) | 7.48(6.30, 8.40) | 5.06(4.14, 6.05) | 68.9(63.7, 75.9) | 2.22(1.75, 3.14) | ||||||
| χ2/Z值 | -14.641 | -3.244 | -3.506 | -1.973 | -1.973 | |||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.048 | 0.048 | |||||||
| 组别 | CRP (mg/L) | PCT (μg/L) | SF (μg/L) | ESR (mm/h) | D-D (mg/L) | LDH (U/L) | ||||||
| n-RMPP | 6.0(5.0, 10.0) | 0.08(0.04, 0.23) | 28.15(14.15, 84.28) | 19.0(8.0, 37.0) | 0.38(0.23, 0.60) | 271.5(201.8, 334.0) | ||||||
| RMPP | 17.0(12.0, 23.0) | 0.60(0.08, 0.86) | 70.50(38.38, 124.38) | 20.0(7.8, 37.0) | 1.15(0.65, 2.51) | 515.0(406.0, 598.0) | ||||||
| χ2/Z值 | -16.451 | -10.117 | -9.527 | -0.229 | -16.447 | -21.048 | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.819 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| LUS(分) | 0.244 | 0.033 | 54.563 | <0.001 | 1.276 | 1.196 | 1.362 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 0.086 | 0.013 | 41.010 | <0.001 | 1.098 | 1.062 | 1.119 |
| D-D(mg/L) | 0.987 | 0.170 | 33.783 | <0.001 | 2.683 | 1.923 | 3.742 |
| LDH(U/L) | 0.015 | 0.001 | 135.117 | <0.001 | 1.015 | 1.013 | 1.018 |
Tab.3 Multivariate logistic regression analysis for different factors on RMPP
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| LUS(分) | 0.244 | 0.033 | 54.563 | <0.001 | 1.276 | 1.196 | 1.362 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 0.086 | 0.013 | 41.010 | <0.001 | 1.098 | 1.062 | 1.119 |
| D-D(mg/L) | 0.987 | 0.170 | 33.783 | <0.001 | 2.683 | 1.923 | 3.742 |
| LDH(U/L) | 0.015 | 0.001 | 135.117 | <0.001 | 1.015 | 1.013 | 1.018 |
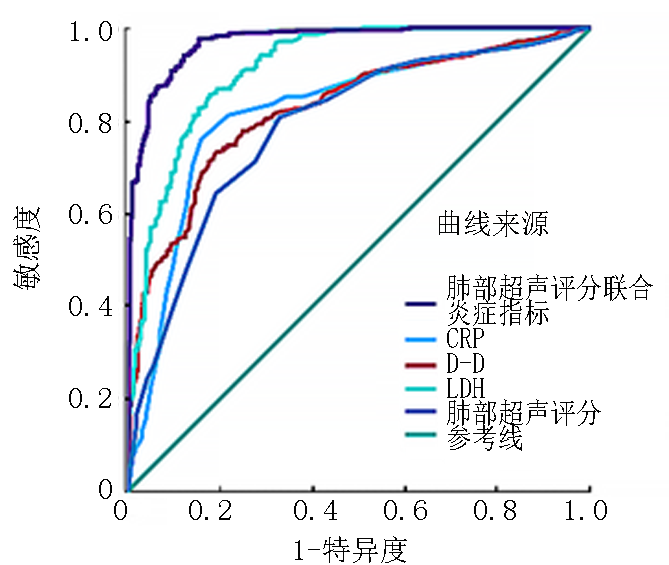
| 指标 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| LUS | 0.788 | <0.001 | 0.757 | 0.818 | 80.7% | 67.2% | 21.5 |
| D-D | 0.824 | <0.001 | 0.797 | 0.851 | 73.1% | 81.0% | 0.745 |
| CRP | 0.821 | <0.001 | 0.791 | 0.850 | 75.9% | 84.1% | 11.5 |
| LDH | 0.915 | <0.001 | 0.896 | 0.934 | 85.5% | 82.3% | 359.5 |
| 联合预测 | 0.969 | <0.001 | 0.958 | 0.979 | 97.4% | 84.7% | 0.638 |
Tab.4 Predictive performance of different variables on RMPP
| 指标 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| LUS | 0.788 | <0.001 | 0.757 | 0.818 | 80.7% | 67.2% | 21.5 |
| D-D | 0.824 | <0.001 | 0.797 | 0.851 | 73.1% | 81.0% | 0.745 |
| CRP | 0.821 | <0.001 | 0.791 | 0.850 | 75.9% | 84.1% | 11.5 |
| LDH | 0.915 | <0.001 | 0.896 | 0.934 | 85.5% | 82.3% | 359.5 |
| 联合预测 | 0.969 | <0.001 | 0.958 | 0.979 | 97.4% | 84.7% | 0.638 |
| [1] | Koenen MH, de Groot RCA, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae carriage in children with recurrent respiratory tract infections is associated with a less diverse and altered microbiota[J]. EBioMedicine, 2023, 98:104868. |
| [2] | Wang X, Li M, Luo M, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae triggers pneumonia epidemic in autumn and winter in Beijing: A multicentre, population-based epidemiological study between 2015 and 2020[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2022, 11(1):1508-1517. |
| [3] | Kim YS, Lee YY, Lee E. Cases of macrolide-resistant mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia-associated pulmonary thromboembolism[J]. Pediatr Pulmonol, 2021, 56(6):1796-1799. |
| [4] |
Yan C, Xue GH, Zhao HQ, et al. Current status of mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in China[J]. World J Pediatr, 2024, 20(1):1-4.
doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00783-x pmid: 38185707 |
| [5] | Li H, Li S, Yang H, et al. Resurgence of mycoplasma pneumonia by macrolide-resistant epidemic clones in China[J]. Lancet Microbe, 2024, 5(6):e515. |
| [6] | Chen YC, Hsu WY, Chang TH. Macrolide-resistant mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in pediatric community-acquired pneumonia[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2020, 26(7):1382-1391. |
| [7] | 徐震. 68例儿童难治性支原体肺炎肺外并发症的临床分析[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2013, 20(3):319-320. |
| [8] | Wen J, Su Y, Sun H, et al. The combination of initial markers to predict refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Chinese children: A case control study[J]. Respir Res, 2021, 22(1):89. |
| [9] |
Bi Y, Zhu Y, Ma X, et al. Development of a scale for early prediction of refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in hospitalized children[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1):6595.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86086-5 pmid: 33758243 |
| [10] | 李宁, 陈言钊, 周克英. 乳酸脱氢酶在儿童难治性肺炎支原体肺炎诊断和治疗中的意义[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2017, 24(4):305-308. |
| [11] | 中华医学会儿科学分会呼吸学组, 中华儿科杂志编辑委员会, 中国医药教育协会儿科专业委员会. 儿童社区获得性肺炎管理指南(2024修订)[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2024, 62(10):920-930. |
| [12] | Chen Y, Li X, Fu Y, et al. Whole-genome sequencing unveils the outbreak of mycoplasma pneumoniae in mainland China[J]. Lancet Microbe, 2024, 5(9):100870. |
| [13] | 于红奎, 刘晓, 陈嘉坤, 等. 肺超声评分对儿童重症肺炎定量评估及预后判断的价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2019, 35(3):229-231. |
| [14] | 赵顺英, 钱素云, 陈志敏, 等. 儿童肺炎支原体肺炎诊疗指南(2023年版)[J]. 新发传染病电子杂志, 2024, 9(1):73-79. |
| [15] | 廖姮, 牛延德, 朱晓娟, 等. 肺部超声诊断儿童社区获得性肺炎动态的价值研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2022, 33(4):240-242+248. |
| [16] | 郭志勇, 蒋钰铖, 张倩仪, 等. 儿童肺炎60例超声检查的临床应用探讨[J]. 实用医学影像杂志, 2022, 23(2):168-171. |
| [17] |
Yang Y, Wu Y, Zhao W. Comparison of lung ultrasound and chest radiography for detecting pneumonia in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ital J Pediatr, 2024, 50(1):12.
doi: 10.1186/s13052-024-01583-3 pmid: 38263086 |
| [18] | 苏姣, 周海艳, 李传芬. 肺部超声评分和CRP对儿童肺炎病情严重程度的预测意义[J]. 中华肺部疾病杂志(电子版), 2021, 14(5):605-607. |
| [19] | Xie W, Ruan J, Jiang Q, et al. Distinguishing types and severity of pediatric pneumonia using modified lung ultrasound score[J]. Front Pediatr, 2024, 12:1411365. |
| [20] | 万钟予, 戚惠霏, 卢燕鸣. 肺部超声评分联合外周血参数比值在儿童重症肺炎支原体肺炎中的意义[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2023, 28(10):1505-1510. |
| [21] | Huang W, Xu X, Zhao W, et al. Refractory mycoplasma pneumonia in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory features and predictors[J]. J Immunol Res, 2022, 2022:9227838. |
| [22] | Pei H, Luo H. Predictive clinical indicators of refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2024, 103(34):e39375. |
| [23] |
Huang X, Li D, Liu F, et al. Clinical significance of D-dimer levels in refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2021, 21(1):14.
doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05700-5 pmid: 33407216 |
| [24] | Wang S, Jiang Z, Li X, et al. Diagnostic value of serum LDH in children with refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumoniae: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Pediatr, 2023, 11:1094118. |
| [1] | Xu Huifeng, Jin Yanyong, Gou Ruolan, Hu Mingzhe. Risk factors for hydrocephalus in children with cerebral hemorrhage and its prediction model [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(4): 325-328. |
| [2] | Zhao Guangyan, Han Tuo, Liang Xiying, Wang Qian, Zhang Yan, Wang Congxia. Risk factors and predictive model for masked hypertension in young and middle-aged adults [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(3): 205-210. |
| [3] | Hu Feifei, Wang Fang, Wang Yongni, Huang Shini, Ming Yao. Risk prediction models for weaning failure from mechanical ventilation: A systematic review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 107-116. |
| [4] | Liu Jinteng, Liu Xingyu, Huang Lumei, Pan Hailong. The risk prediction models for pneumonia in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(1): 5-13. |
| [5] | Zhu Jieyun, Gao Min, Huang Chunli, Pan Dongzan, Wang Qiaoyan, Lu Zhao. Risk prediction model for readmission of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 773-779. |
| [6] | Wu Qiupin, Yan Shiwei, He Xiaoyin, Li Yun, LU Liju, Wu Yi. Analysis of hepatitis associated aplastic anemia in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 640-643. |
| [7] | Wu Weijun, Chen Xiao, Wang Shaodan, Bu Laijun, Wu Xinchao, Yan Chenyang, Dong Gaiqin, Jiang Lijun, Wei Wenping. Analysis of screening data of urinalysis in 1973 students in Yangzhou [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 702-705. |
| [8] | Chen Congshui, Li Yuan, Chen Shufang. Concerning the diagnosis and integrated Chinese and Western medicine treatment of acute biliary pancreatitis in children: A case report [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 726-730. |
| [9] | Sun Xingxing, Lin Hai. Changes in immune function and prognostic risk factors for severe pneumonia in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(6): 521-525. |
| [10] | Liu Yuqing, Cheng Ji. Familial Holt-Oram syndrome: Report of a case & literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(1): 71-74. |
| [11] | Hu Wencong, Liu Xiuzhen. Two cases of children's anti-MOG antibodies combined with anti-NMDAR antibody double positive autoimmune encephalitis and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(8): 733-737. |
| [12] | Yu Xin, Liu Zhongyang. Predictive value of lung ultrasonography on adjusted therapeutic regimen for patients with pneumonia [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(2): 133-136. |
| [13] | Yu Jinghong, Zhao Yan, Yu Shufeng, Wang Caixia. Investigation and analysis on helicobacter pylori infection of children in Qingdao region [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(2): 141-144. |
| [14] | Hou Wei, Zhang Lijun, Zhang Man, Wang Yakun, Jia Meixuan, Tian Liyuan. Clinical analysis in 84 children with the sepsis of non-elevated peripheral blood leukocytes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(9): 799-802. |
| [15] | Meng Luming, Mao Luyi, He Muyan, Zhang Qiuyan. Value of the combination of PCT, CRP, and IL-8 to predict the effect of hormonal intervention in children with bronchitis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(10): 942-945. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||