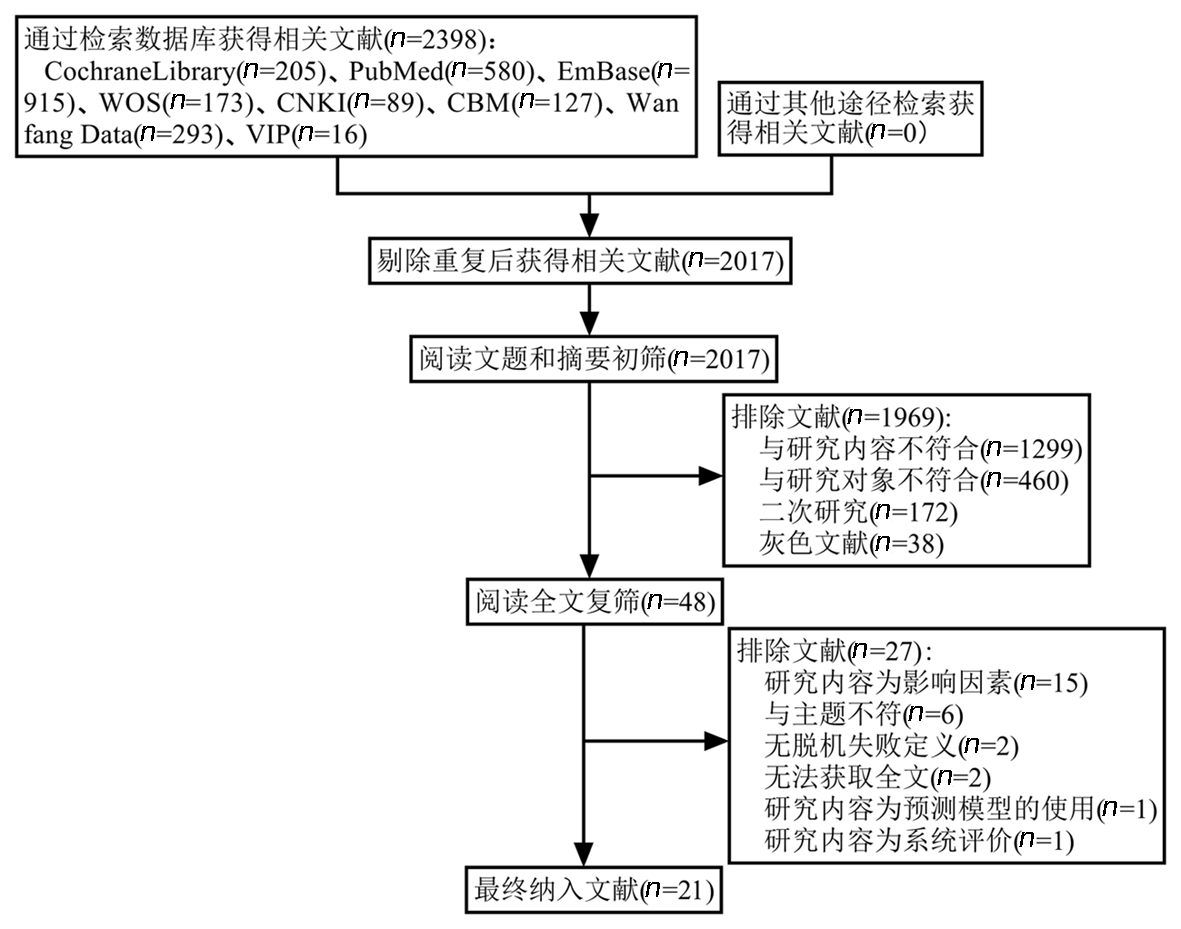
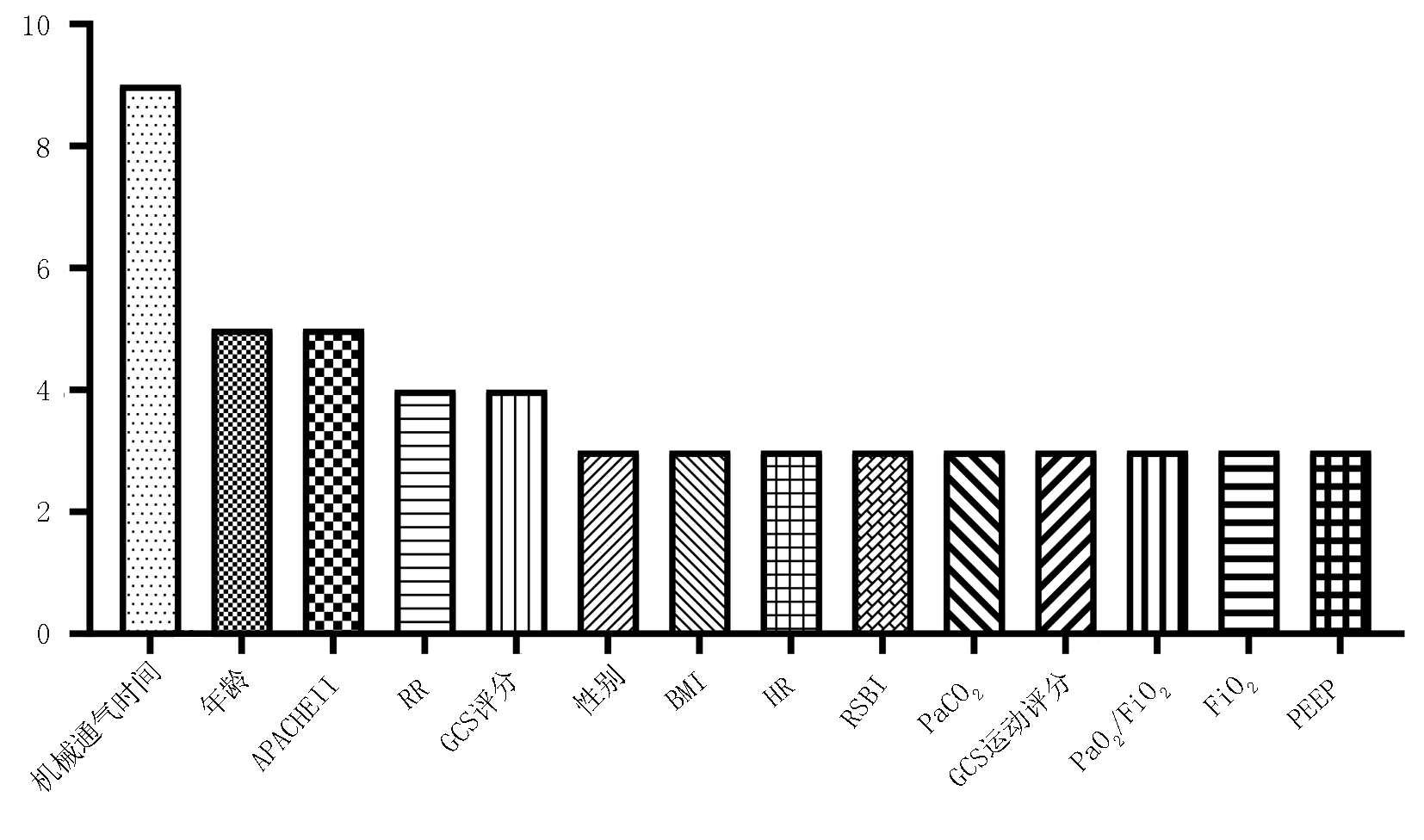
Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 107-116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.02.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Risk prediction models for weaning failure from mechanical ventilation: A systematic review
Hu Feifei1, Wang Fang2( ), Wang Yongni1, Huang Shini1, Ming Yao1
), Wang Yongni1, Huang Shini1, Ming Yao1
- 1. School of Nursing, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
2. Guang'an Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guang'an 638001, China
-
Received:2024-12-03Online:2025-02-20Published:2025-03-04 -
Contact:Wang Fang E-mail:1697070757@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Feifei, Wang Fang, Wang Yongni, Huang Shini, Ming Yao. Risk prediction models for weaning failure from mechanical ventilation: A systematic review[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 107-116.
share this article
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 研究类型 | 研究对象 | 数据来源 | 脱机失败结局定义 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kuo等[ | 中国台湾 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 台北市2家医院 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | 哥伦比亚 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 麦德林临床重症监护室 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Godet等[ | 法国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 克莱蒙费朗大学医院 | 在ICU住院期间均需要有创机械通气支持 |
| Dos Reis等[ | 巴西 | 回顾性研究 | 创伤性脑损伤患者 | 巴伊亚州综合医院 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Hsieh等[ | 美国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 奇美医疗中心 | 计划拔管后72 h内重新插管或死亡 |
| Chung等[ | 中国台湾 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 台湾高雄医学大学医院 | 拔管后重新插管或在48 h内发生呼吸衰竭 |
| Yan等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | MIMIC-IV V.1.0数据库 | SBT失败,或脱机后48 h内需要重新插管,或48 h内死亡 |
| Liu等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | 脓毒症患者 | MIMIC-IV V.1.0数据库和eICU-CRD(2.0)数据库 | 脱机48 h内恢复有创机械通气或48 h内死亡 |
| Chen等[ | 中国台湾 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 郑新综合医院 | 拔管后24 h内需要重新插管 |
| Liu等[ | 中国台湾 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 奇美医疗中心 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Cinotti等[ | 多国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 18个国家的73个重症监护病房 | 脱机失败的时间范围为5 d |
| Kim等[ | 韩国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | MIMIC-IV V.1.0数据库 | 插管14 d内脱机失败或发生死亡 |
| Schreiber等[ | 加拿大 | 回顾性研究 | 创伤性脊髓损伤患者 | 圣迈克尔医院和里克·汉森研究所 | 患者在离开ICU时仍需要有创机械通气支持 |
| Menguy等[ | 法国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | ReaSTOC数据库 | SBT失败或72 h内再次插管 |
| Kim等[ | 韩国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 忠北国立大学医院 | SBT期间出现呼吸窘迫,或SBT后重新插管 |
| 赵文婷等[ | 中国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 淮安市第二人民医院重症医学科 | 脱机48 h内死亡或48 h内内重新插管 |
| 杨晓文等[ | 中国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 江苏省人民医院 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| 王建华等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 潍坊市人民医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
| 颜瑶等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | MIMIC-ⅣV.1.0数据库、连云港市第一人民医院和连云港市第二人民医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
| Zhang等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | 心脏体外循环术后患者 | 南京医科大学第一附属医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
| Xu等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 连云港市第二人民医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
Tab. 1 Basic characteristics of the included literature
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 研究类型 | 研究对象 | 数据来源 | 脱机失败结局定义 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kuo等[ | 中国台湾 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 台北市2家医院 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | 哥伦比亚 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 麦德林临床重症监护室 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Godet等[ | 法国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 克莱蒙费朗大学医院 | 在ICU住院期间均需要有创机械通气支持 |
| Dos Reis等[ | 巴西 | 回顾性研究 | 创伤性脑损伤患者 | 巴伊亚州综合医院 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Hsieh等[ | 美国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 奇美医疗中心 | 计划拔管后72 h内重新插管或死亡 |
| Chung等[ | 中国台湾 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 台湾高雄医学大学医院 | 拔管后重新插管或在48 h内发生呼吸衰竭 |
| Yan等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | MIMIC-IV V.1.0数据库 | SBT失败,或脱机后48 h内需要重新插管,或48 h内死亡 |
| Liu等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | 脓毒症患者 | MIMIC-IV V.1.0数据库和eICU-CRD(2.0)数据库 | 脱机48 h内恢复有创机械通气或48 h内死亡 |
| Chen等[ | 中国台湾 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 郑新综合医院 | 拔管后24 h内需要重新插管 |
| Liu等[ | 中国台湾 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 奇美医疗中心 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| Cinotti等[ | 多国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 18个国家的73个重症监护病房 | 脱机失败的时间范围为5 d |
| Kim等[ | 韩国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | MIMIC-IV V.1.0数据库 | 插管14 d内脱机失败或发生死亡 |
| Schreiber等[ | 加拿大 | 回顾性研究 | 创伤性脊髓损伤患者 | 圣迈克尔医院和里克·汉森研究所 | 患者在离开ICU时仍需要有创机械通气支持 |
| Menguy等[ | 法国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | ReaSTOC数据库 | SBT失败或72 h内再次插管 |
| Kim等[ | 韩国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 忠北国立大学医院 | SBT期间出现呼吸窘迫,或SBT后重新插管 |
| 赵文婷等[ | 中国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 淮安市第二人民医院重症医学科 | 脱机48 h内死亡或48 h内内重新插管 |
| 杨晓文等[ | 中国 | 前瞻性研究 | ICU患者 | 江苏省人民医院 | 拔管后48 h内需要重新插管 |
| 王建华等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 潍坊市人民医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
| 颜瑶等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | MIMIC-ⅣV.1.0数据库、连云港市第一人民医院和连云港市第二人民医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
| Zhang等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | 心脏体外循环术后患者 | 南京医科大学第一附属医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
| Xu等[ | 中国 | 回顾性研究 | ICU患者 | 连云港市第二人民医院 | SBT失败或脱机48 h内重新插管或48 h内死亡 |
| 纳入文献 | 候选变量 | 样本量(例) | 结局事件比例(%) | 缺失数据 | 建模方法 | 变量选择 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 候选变量 数量(个) | 连续变量 处理方法 | 建模组 | 验证组 (内部/外部) | 建模组 | 验证组 (内部/外部) | 数量(例) | 处理方式 | ||||||
| Kuo等[ | 8 | 保持连续性 | 76 | 45/- | 26.3% | 24.4%/- | - | - | 人工神经网络 | 文献回顾、临床应用便利性 | |||
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | 13 | 保持连续性 | 1017 | -/- | 15.4% | -/- | 8 | 插补法 | Logistic回归 | 向前和向后逐步选择法 | |||
| Godet等[ | 10 | 保持连续性 | 140 | -/- | 30.7% | -/- | 1276 | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Dos Reis等[ | 17 | 部分保持连续性 | 311 | -/- | 13.8% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Hsieh等[ | 37 | 保持连续性 | 3602 | -/- | 5.1% | -/- | - | - | 人工神经网络 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Chung等[ | - | 保持连续性 | 169 | -/- | 16.6% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 逐步选择法 | |||
| Yan等[ | 32 | 部分保持连续性 | 2586 | 1109/- | 38.8% | 38.4%/- | - | 数据缺失率>15%直接删除;数据缺失率<15%多重插补 | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Liu等[ | 20 | 保持连续性 | 4016 | 1004/7081 | 43.0% | -/13.2% | 6486/27294 | 多重插补 | KNN、MLP、RF、SVM、LR、XGBoost, 中XGBoost最佳 | 临床重要性和shapley加性解释 | |||
| Chen等[ | 28 | 保持连续性 | 1042 | -/- | 38.1% | -/- | - | - | LR、DT、RF、XGBoost、SVM和ANN,其中XGBoost和LR最佳 | 向前向后逐步选择 | |||
| Liu等[ | 20 | 保持连续性 | 4172 | -/- | 48.9% | -/- | - | - | LR、RF、SVM、KNN、lightGBM、XGBoost、MLP,其中lightGBM最佳 | 文献回顾、临床经验和实用性 | |||
| Cinotti等[ | 20 | 保持连续性 | 737 | 369/- | 41.8% | 45.0%/- | - | 多重插补 | Logistic回归 | 文献回顾和Lasso回归 | |||
| Kim等[ | 46 | 保持连续性 | 23242 | -/- | 18.1% | -/- | - | 多重插补和K邻近法 | RLRC、RF、CBC、VC,其中VC最佳 | Shapley加性解释 | |||
| Schreiber等[ | 16 | 保持连续性 | 459 | -/- | 27.9% | -/- | - | 多重插补 | Logistic回归 | Lasso回归 | |||
| Menguy等[ | - | 部分保持连续性 | 135 | -/- | 50.37% | -/- | - | - | 基于人工智能和机器学习ZGPDmodel | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Kim等[ | 18 | 保持连续性 | 1041 | -/- | 38.4% | -/- | - | - | 图形神经网络 | 文献回顾 | |||
| 赵文婷等[ | 22 | 部分保持连续性 | 469 | 201/- | 18.8% | 22.4%/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| 杨晓文等[ | 12 | 部分保持连续性 | 310 | -/- | 19.35% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| 王建华等[ | 28 | 保持连续性 | 358 | 188/- | 21.8% | 28.2%/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 文献回顾与专家咨询后先单因素分析再多因素分析 | |||
| 颜瑶等[ | 27 | 保持连续性 | 3695 | -/292 | 38.5% | -/35.3% | 缺失率>10% 的数据 | 删除 | Logistic回归 | Lasso回归 | |||
| Zhang等[ | 55 | 保持连续性 | 519 | -/- | 16.6% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析和Lasso回归 | |||
| Xu等[ | 34 | 保持连续性 | 341 | 146/- | 20.5% | 22.6%/- | - | - | LR、SVM、RF、XG boost、Light GBM其中RF最佳 | 单因素分析 | |||
Tab. 2 Predictive modeling of the risk of weaning failure in mechanically ventilated patients
| 纳入文献 | 候选变量 | 样本量(例) | 结局事件比例(%) | 缺失数据 | 建模方法 | 变量选择 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 候选变量 数量(个) | 连续变量 处理方法 | 建模组 | 验证组 (内部/外部) | 建模组 | 验证组 (内部/外部) | 数量(例) | 处理方式 | ||||||
| Kuo等[ | 8 | 保持连续性 | 76 | 45/- | 26.3% | 24.4%/- | - | - | 人工神经网络 | 文献回顾、临床应用便利性 | |||
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | 13 | 保持连续性 | 1017 | -/- | 15.4% | -/- | 8 | 插补法 | Logistic回归 | 向前和向后逐步选择法 | |||
| Godet等[ | 10 | 保持连续性 | 140 | -/- | 30.7% | -/- | 1276 | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Dos Reis等[ | 17 | 部分保持连续性 | 311 | -/- | 13.8% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Hsieh等[ | 37 | 保持连续性 | 3602 | -/- | 5.1% | -/- | - | - | 人工神经网络 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Chung等[ | - | 保持连续性 | 169 | -/- | 16.6% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 逐步选择法 | |||
| Yan等[ | 32 | 部分保持连续性 | 2586 | 1109/- | 38.8% | 38.4%/- | - | 数据缺失率>15%直接删除;数据缺失率<15%多重插补 | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Liu等[ | 20 | 保持连续性 | 4016 | 1004/7081 | 43.0% | -/13.2% | 6486/27294 | 多重插补 | KNN、MLP、RF、SVM、LR、XGBoost, 中XGBoost最佳 | 临床重要性和shapley加性解释 | |||
| Chen等[ | 28 | 保持连续性 | 1042 | -/- | 38.1% | -/- | - | - | LR、DT、RF、XGBoost、SVM和ANN,其中XGBoost和LR最佳 | 向前向后逐步选择 | |||
| Liu等[ | 20 | 保持连续性 | 4172 | -/- | 48.9% | -/- | - | - | LR、RF、SVM、KNN、lightGBM、XGBoost、MLP,其中lightGBM最佳 | 文献回顾、临床经验和实用性 | |||
| Cinotti等[ | 20 | 保持连续性 | 737 | 369/- | 41.8% | 45.0%/- | - | 多重插补 | Logistic回归 | 文献回顾和Lasso回归 | |||
| Kim等[ | 46 | 保持连续性 | 23242 | -/- | 18.1% | -/- | - | 多重插补和K邻近法 | RLRC、RF、CBC、VC,其中VC最佳 | Shapley加性解释 | |||
| Schreiber等[ | 16 | 保持连续性 | 459 | -/- | 27.9% | -/- | - | 多重插补 | Logistic回归 | Lasso回归 | |||
| Menguy等[ | - | 部分保持连续性 | 135 | -/- | 50.37% | -/- | - | - | 基于人工智能和机器学习ZGPDmodel | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| Kim等[ | 18 | 保持连续性 | 1041 | -/- | 38.4% | -/- | - | - | 图形神经网络 | 文献回顾 | |||
| 赵文婷等[ | 22 | 部分保持连续性 | 469 | 201/- | 18.8% | 22.4%/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| 杨晓文等[ | 12 | 部分保持连续性 | 310 | -/- | 19.35% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析后采用多因素分析 | |||
| 王建华等[ | 28 | 保持连续性 | 358 | 188/- | 21.8% | 28.2%/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 文献回顾与专家咨询后先单因素分析再多因素分析 | |||
| 颜瑶等[ | 27 | 保持连续性 | 3695 | -/292 | 38.5% | -/35.3% | 缺失率>10% 的数据 | 删除 | Logistic回归 | Lasso回归 | |||
| Zhang等[ | 55 | 保持连续性 | 519 | -/- | 16.6% | -/- | - | - | Logistic回归 | 单因素分析和Lasso回归 | |||
| Xu等[ | 34 | 保持连续性 | 341 | 146/- | 20.5% | 22.6%/- | - | - | LR、SVM、RF、XG boost、Light GBM其中RF最佳 | 单因素分析 | |||
| 纳入研究 | 模型性能 | 验模方式 | 模型呈现方式 | 预测因子 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | 校准方法 | ||||
| Kuo等[ | 建模组:0.83 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、五折交叉验证) | 风险计算公式 | RSBI、PImax、RSBI1、RSBI30和ΔRSBI30 |
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | 0.689 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 风险计算公式 | BUN、氧合指数、APACHE II、累积液体平衡和血红蛋白 |
| Godet等[ | 0.82 | - | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 风险评分 | 咳嗽反应、吞咽能力、吞咽反射、CRS视觉评分 |
| Dos Reis等[ | 0.81 | H-L检验(P=0.78) | - | 风险评分 | 女性、GCS运动评分、分泌物、咳嗽反应、机械通气持续时间 |
| Hsieh等[ | 验模组:0.85 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、K折交叉验证) | - | TISS评分、血液透析、RSBI、拔管前心率、拔管前氧合指数和MEP |
| Chung等[ | 0.889 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证) | 风险计算公式 | 性别;身高;SpO2;GCS;APACHE II分数、肺部疾病史;SBT时第一分钟、第30分钟、第60分钟和第90分钟的VE、RR、VT |
| Yan等[ | 建模组:0.828 验模组:0.833 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、Bootstrap法) | 列线图 | PEEP、MP、Cdyn、FiO2、ICU住院时间、机械通气时间 |
| Liu等[ | 模型一:内部验证:0.80,外部验证:0.86 模型二:内部验证:0.75,外部验证:0.78 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(随机拆分验证)+外部验证 | web在线预测工具 | 模型1:尿量、最低碱过量、GCS、最低SPO2、充血性心力衰竭、最低pH值、最低map、最高PaCO2、肾脏疾病、最低血小板计数、BMI和氧合指数 模型2:机械通气持续时间、最高PEEP水平、尿量和最低碱过量 |
| Chen等[ | 0.86 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、十折交叉验证) | 风险计算公式 | ExpMV、ExpTV、VenRS、心率、PeakPr、pH和年龄 |
| Liu等[ | 0.923 | - | 内部验证(五折交叉验证) | 数字仪表板预测系统 | 吸痰频率、SBT次数、GCS运动评分、APACHE II评分、PSLvolume、RR |
| Cinotti等[ | 建模组:0.79 验模组:0.71 | 校准曲线和H-L检验 | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、十折交叉验证) | 风险评分 | TBI、剧烈咳嗽、呕吐反射、吞咽能力、气管内吸引≤每小时2次、GCS运动评分和拔管当天的体温 |
| Kim等[ | 0.861 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(五折交叉验证) | - | 主要因素包括阴离子间隙、年龄、脑血管疾病和BUN等 |
| Schreiber等[ | 0.689 | - | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 风险计算公式 | 钝性作为原发性损伤为钝性、年龄、损伤严重性评分、颈椎病变、完全性综合征 |
| Menguy等[ | - | - | - | web在线预测工具 | BMI、SBT前测量的P0.1、SBT前的LF/HF和SBT期间的心率 |
| Kim等[ | 0.87 | - | 内部验证(四折交叉验证) | 图形结构 | 机械通气时间、呼吸频率、氧合指数、PaCO2、GCS、FiO2、年龄、BMI、性别、通气模式 |
| 赵文婷等[ | 建模组:0.870; 验模组:0.867 | 校准曲线和H-L检验(建模组P=0.468;验模组P=0.487) | 内部验证(随机拆分验证) | 列线图 | 机械通气时间、APACHEⅡ评分、SOFA评分、通气后PaCO2、VIDD |
| 杨晓文等[ | 0.722 | H-L检验(P=0.438) | - | 风险计算公式 | 年龄、GCS评分、吸烟指数、机械通气时间、MODS及呼吸系统基础疾病 |
| 王建华等[ | 建模组:0.926 验模组:0.924 | H-L检验(P=0.629) | 内部验证(随机拆分验证) | 风险计算公式 | 机械通气时间、膈肌移动度、膈肌厚度变异率、RSBI、下腔静脉变异度 |
| 颜瑶等[ | 建模组:0.832; 外部验证组:0.879 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(Bootstrap法)+外部验证 | 列线图 | PEEP、MP、Cdyn、FiO2、ICU住院时间、机械通气时间 |
| Zhang等[ | 0.864 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 列线图 | 撤机前VVR评分、撤机前机械通气持续时间、撤机当天mSOFA评分 |
| Xu等[ | 建模组:0.805 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(五折交叉验证) | 风险计算公式 | APACHEII、SBT时RR、GCS评分、血红蛋白 |
Tab. 3 Performance and predictors of risk predictive model for weaning failure in mechanically ventilated patients
| 纳入研究 | 模型性能 | 验模方式 | 模型呈现方式 | 预测因子 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | 校准方法 | ||||
| Kuo等[ | 建模组:0.83 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、五折交叉验证) | 风险计算公式 | RSBI、PImax、RSBI1、RSBI30和ΔRSBI30 |
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | 0.689 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 风险计算公式 | BUN、氧合指数、APACHE II、累积液体平衡和血红蛋白 |
| Godet等[ | 0.82 | - | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 风险评分 | 咳嗽反应、吞咽能力、吞咽反射、CRS视觉评分 |
| Dos Reis等[ | 0.81 | H-L检验(P=0.78) | - | 风险评分 | 女性、GCS运动评分、分泌物、咳嗽反应、机械通气持续时间 |
| Hsieh等[ | 验模组:0.85 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、K折交叉验证) | - | TISS评分、血液透析、RSBI、拔管前心率、拔管前氧合指数和MEP |
| Chung等[ | 0.889 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证) | 风险计算公式 | 性别;身高;SpO2;GCS;APACHE II分数、肺部疾病史;SBT时第一分钟、第30分钟、第60分钟和第90分钟的VE、RR、VT |
| Yan等[ | 建模组:0.828 验模组:0.833 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、Bootstrap法) | 列线图 | PEEP、MP、Cdyn、FiO2、ICU住院时间、机械通气时间 |
| Liu等[ | 模型一:内部验证:0.80,外部验证:0.86 模型二:内部验证:0.75,外部验证:0.78 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(随机拆分验证)+外部验证 | web在线预测工具 | 模型1:尿量、最低碱过量、GCS、最低SPO2、充血性心力衰竭、最低pH值、最低map、最高PaCO2、肾脏疾病、最低血小板计数、BMI和氧合指数 模型2:机械通气持续时间、最高PEEP水平、尿量和最低碱过量 |
| Chen等[ | 0.86 | - | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、十折交叉验证) | 风险计算公式 | ExpMV、ExpTV、VenRS、心率、PeakPr、pH和年龄 |
| Liu等[ | 0.923 | - | 内部验证(五折交叉验证) | 数字仪表板预测系统 | 吸痰频率、SBT次数、GCS运动评分、APACHE II评分、PSLvolume、RR |
| Cinotti等[ | 建模组:0.79 验模组:0.71 | 校准曲线和H-L检验 | 内部验证(随机拆分验证、十折交叉验证) | 风险评分 | TBI、剧烈咳嗽、呕吐反射、吞咽能力、气管内吸引≤每小时2次、GCS运动评分和拔管当天的体温 |
| Kim等[ | 0.861 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(五折交叉验证) | - | 主要因素包括阴离子间隙、年龄、脑血管疾病和BUN等 |
| Schreiber等[ | 0.689 | - | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 风险计算公式 | 钝性作为原发性损伤为钝性、年龄、损伤严重性评分、颈椎病变、完全性综合征 |
| Menguy等[ | - | - | - | web在线预测工具 | BMI、SBT前测量的P0.1、SBT前的LF/HF和SBT期间的心率 |
| Kim等[ | 0.87 | - | 内部验证(四折交叉验证) | 图形结构 | 机械通气时间、呼吸频率、氧合指数、PaCO2、GCS、FiO2、年龄、BMI、性别、通气模式 |
| 赵文婷等[ | 建模组:0.870; 验模组:0.867 | 校准曲线和H-L检验(建模组P=0.468;验模组P=0.487) | 内部验证(随机拆分验证) | 列线图 | 机械通气时间、APACHEⅡ评分、SOFA评分、通气后PaCO2、VIDD |
| 杨晓文等[ | 0.722 | H-L检验(P=0.438) | - | 风险计算公式 | 年龄、GCS评分、吸烟指数、机械通气时间、MODS及呼吸系统基础疾病 |
| 王建华等[ | 建模组:0.926 验模组:0.924 | H-L检验(P=0.629) | 内部验证(随机拆分验证) | 风险计算公式 | 机械通气时间、膈肌移动度、膈肌厚度变异率、RSBI、下腔静脉变异度 |
| 颜瑶等[ | 建模组:0.832; 外部验证组:0.879 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(Bootstrap法)+外部验证 | 列线图 | PEEP、MP、Cdyn、FiO2、ICU住院时间、机械通气时间 |
| Zhang等[ | 0.864 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(Bootstrap法) | 列线图 | 撤机前VVR评分、撤机前机械通气持续时间、撤机当天mSOFA评分 |
| Xu等[ | 建模组:0.805 | 校准曲线 | 内部验证(五折交叉验证) | 风险计算公式 | APACHEII、SBT时RR、GCS评分、血红蛋白 |
| 纳入研究 | 偏倚风险 | 适用性 | 总体 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究对象 | 预测因子 | 结局 | 分析 | 研究对象 | 预测因子 | 结局 | 偏倚风险 | 适用性 | |||||||||
| Kuo等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | - | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Godet等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Dos Reis等[ | - | ? | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Hsieh等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Chung等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Yan等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Liu等[ | - | ? | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Chen等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Liu等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Cinotti等[ | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | + | ||||||||
| Kim等[ | - | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Schreiber等[ | - | ? | ? | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Menguy等[ | + | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Kim等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 赵文婷等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 杨晓文等[ | + | + | ? | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 王建华等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 颜瑶等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Zhang等[ | - | ? | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Xu等[ | - | ? | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
Tab. 4 Evaluation for risk of bias and applicability of included studies
| 纳入研究 | 偏倚风险 | 适用性 | 总体 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究对象 | 预测因子 | 结局 | 分析 | 研究对象 | 预测因子 | 结局 | 偏倚风险 | 适用性 | |||||||||
| Kuo等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Sará-Ochoa等[ | - | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Godet等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Dos Reis等[ | - | ? | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Hsieh等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Chung等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Yan等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Liu等[ | - | ? | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Chen等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Liu等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Cinotti等[ | + | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | ? | + | ||||||||
| Kim等[ | - | ? | + | ? | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Schreiber等[ | - | ? | ? | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Menguy等[ | + | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Kim等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 赵文婷等[ | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 杨晓文等[ | + | + | ? | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 王建华等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| 颜瑶等[ | - | ? | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| Zhang等[ | - | ? | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | ||||||||
| Xu等[ | - | ? | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | ||||||||
| [1] |
Wunsch H, Wagner J, Herlim M, et al. ICU occupancy and mechanical ventilator use in the United States[J]. Crit Care Med, 2013, 41(12): 2712-2719.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318298a139 pmid: 23963122 |
| [2] |
Needham DM, Bronskill SE, Calinawan JR, et al. Projected incidence of mechanical ventilation in ontario to 2026: Preparing for the aging baby boomers[J]. Crit Care Med, 2005, 33(3): 574-579.
pmid: 15753749 |
| [3] |
Ouellette DR, Patel S, Girard TD, et al. Liberation from mechanical ventilation in critically ill adults: An official american college of chest physicians/american thoracic society clinical practice guideline: Inspiratory pressure augmentation during spontaneous breathing trials, protocols minimizing sedation, and noninvasive ventilation immediately after extubation[J]. Chest, 2017, 151(1): 166-180.
doi: S0012-3692(16)62324-3 pmid: 27818331 |
| [4] |
Burns KEA, Rizvi L, Cook DJ, et al. Ventilator weaning and discontinuation practices for critically ill patients[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(12): 1173-1184.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.2384 pmid: 33755077 |
| [5] |
Pham T, Heunks L, Bellani G, et al. Weaning from mechanical ventilation in intensive care units across 50 countries (WEAN SAFE): A multicentre, prospective, observational cohort study[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2023, 11(5): 465-476.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00449-0 pmid: 36693401 |
| [6] | Jaber S, Quintard H, Cinotti R, et al. Risk factors and outcomes for airway failure versus non-airway failure in the intensive care unit: A multicenter observational study of 1514 extubation procedures[J]. Crit Care, 2018, 22(1): 236. |
| [7] | Shi J, Huan X, Lv Z, et al. Pneumonia and systemic inflammatory response syndrome as predictors for difficult-/prolonged-weaning after invasive ventilation in myasthenic crisis: A retrospective analysis of a chinese cohort[J]. Neuromuscul Disord, 2022, 32(3): 220-229. |
| [8] | Michels JD, Trudzinski FC, Bornitz F, et al. Costs of weaning failure: A prospective, multicentre, controlled, non-randomised, interventional study on economic implications for the german health care system[J]. Respiration, 2023, 102(9): 813-820. |
| [9] | Tanaka A, Shimomura Y, Uchiyama A, et al. Time definition of reintubation most relevant to patient outcomes in critically ill patients: A multicenter cohort study[J]. Crit Care, 2023, 27(1): 378. |
| [10] | Moons KG, Hooft L, Williams K, et al. Implementing systematic reviews of prognosis studies in cochrane[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2018, 10(10): ED000129. |
| [11] | Moons KGM, de Groot JAH, Bouwmeester W, et al. Critical appraisal and data extraction for systematic reviews of prediction modelling studies: The CHARMS checklist[J]. PLoS Med, 2014, 11(10): e1001744. |
| [12] | Moons KGM, Wolff RF, Riley RD, et al. PROBAST: A tool to assess risk of bias and applicability of prediction model studies: Explanation and elaboration[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2019, 170(1): W1-W33. |
| [13] | 陈香萍, 张奕, 庄一渝, 等. PROBAST:诊断或预后多因素预测模型研究偏倚风险的评估工具[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2020, 20(6): 737-744. |
| [14] | Kuo HJ, Chiu HW, Lee CN, et al. Improvement in the prediction of ventilator weaning outcomes by an artificial neural network in a medical ICU[J]. Respir Care, 2015, 60(11): 1560-1569. |
| [15] | Sará-Ochoa JE, Hernández Ortíz OH, Jaimes FA. Development of a predictive model for extubation failure in weaning from mechanical ventilation: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Trends Anaesth Crit Care, 2017, 17: 21-26. |
| [16] |
Godet T, Chabanne R, Marin J, et al. Extubation failure in brain-injured patients: Risk factors and development of a prediction score in a preliminary prospective cohort study[J]. Anesthesiology, 2017, 126(1): 104-114.
pmid: 27749290 |
| [17] |
Dos Reis HFC, Gomes-Neto M, Almeida MLO, et al. Development of a risk score to predict extubation failure in patients with traumatic brain injury[J]. J Crit Care, 2017, 42: 218-222.
doi: S0883-9441(17)30810-9 pmid: 28780488 |
| [18] | Hsieh MH, Hsieh MJ, Chen CM, et al. An artificial neural network model for predicting successful extubation in intensive care units[J]. J Clin Med, 2018, 7(9): 240. |
| [19] | Chung WC, Sheu CC, Hung JY, et al. Novel mechanical ventilator weaning predictive model[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2020, 36(10): 841-849. |
| [20] | Yan Y, Luo J, Wang Y, et al. Development and validation of a mechanical power-oriented prediction model of weaning failure in mechanically ventilated patients: A retrospective cohort study[J]. BMJ Open, 2022, 12(12): e066894. |
| [21] | Liu W, Tao G, Zhang Y, et al. A simple weaning model based on interpretable machine learning algorithm for patients with sepsis: A research of MIMIC-IV and eICU databases[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2022, 8: 814566. |
| [22] | Chen WT, Huang HL, Ko PS, et al. A simple algorithm using ventilator parameters to predict successfully rapid weaning program in cardiac intensive care unit patients[J]. J Pers Med, 2022, 12(3): 501. |
| [23] | Liu CF, Hung CM, Ko SC, et al. An artificial intelligence system to predict the optimal timing for mechanical ventilation weaning for intensive care unit patients: A two-stage prediction approach[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2022, 9: 935366. |
| [24] |
Cinotti R, Mijangos JC, Pelosi P, et al. Extubation in neurocritical care patients: The ENIO international prospective study[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2022, 48(11): 1539-1550.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06825-8 pmid: 36038713 |
| [25] | Kim J, Kim YK, Kim H, et al. Machine learning algorithms predict successful weaning from mechanical ventilation before intubation: Retrospective analysis from the medical information mart for intensive care IV database[J]. JMIR Form Res, 2023, 7: e44763. |
| [26] | Schreiber AF, Garlasco J, Urner M, et al. Mechanical ventilation after traumatic spinal cord injury-a multicentric cohort study-based prediction model for weaning success: The BICYCLE score[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc, 2023, 20(8): 1156-1165. |
| [27] | Menguy J, De Longeaux K, Bodenes L, et al. Defining predictors for successful mechanical ventilation weaning, using a data-mining process and artificial intelligence[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 20483. |
| [28] | Kim GH, Kim JW, Kim KH, et al. FT-GAT: Graph neural network for predicting spontaneous breathing trial success in patients with mechanical ventilation[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2023, 240: 107673. |
| [29] | 赵文婷, 周大文, 杨晓梅, 等. 重症机械通气患者脱机失败的风险预测列线图模型构建与验证[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2023, 31(8): 59-65. |
| [30] | 杨晓文, 童孜蓉, 吴娟, 等. 神经外科重症机械通气患者脱机失败预测模型的构建[J]. 军事护理, 2023, 40(6): 9-12. |
| [31] | 王建华, 孙淑青, 张效东, 等. ICU机械通气患者撤机风险预测模型的构建[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2023, (12): 86-93. |
| [32] | 颜瑶, 谢永鹏, 骆继业, 等. 以机械功为导向预测机械通气患者撤机失败风险列线图模型的建立和验证[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2023, 35(7): 707-713. |
| [33] | Zhang Z, Tang W, Ren Y, et al. Prediction of ventilator weaning failure in postoperative cardiac surgery patients using vasoactive-ventilation-renal score and nomogram analysis[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2024, 11: 1364211. |
| [34] |
Xu H, Ma Y, Zhuang Y, et al. Machine learning-based risk prediction model construction of difficult weaning in ICU patients with mechanical ventilation[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 20875.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71548-3 pmid: 39242766 |
| [35] |
Mandrekar JN. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2010, 5(9): 1315-1316.
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ec173d pmid: 20736804 |
| [36] |
Berger D, Bloechlinger S, von Haehling S, et al. Dysfunction of respiratory muscles in critically ill patients on the intensive care unit[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2016, 7(4): 403-412.
doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12108 pmid: 27030815 |
| [37] | Trudzinski FC, Michels-Zetsche JD, Neetz B, et al. Risk factors for long-term invasive mechanical ventilation: A longitudinal study using german health claims data[J]. Respir Res, 2024, 25(1): 60. |
| [38] | Li W, Zhang Y, Wang Z, et al. The risk factors of reintubation in intensive care unit patients on mechanical ventilation: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Intensive Crit Care Nurs, 2023, 74: 103340. |
| [39] |
Li S, Chen Z, Yan W. Application of bedside ultrasound in predicting the outcome of weaning from mechanical ventilation in elderly patients[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2021, 21(1): 217.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01605-4 pmid: 34243739 |
| [40] | Ghiani A, Tsitouras K, Paderewska J, et al. Incidence, causes, and predictors of unsuccessful decannulation following prolonged weaning[J]. Ther Adv Chronic Dis, 2022, 13: 20406223221109655. |
| [41] | Yu H, Luo J, Ni Y, et al. Early prediction of extubation failure in patients with severe pneumonia: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(2): BSR20192435. |
| [42] | Zhao F, Wang M, Zhou Q, et al. Analysis of risk factors for weaning failure from mechanical ventilation in critically ill older patients with coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(12): e32835. |
| [43] |
Thille AW, Boissier F, Coudroy R, et al. Sex difference in the risk of extubation failure in ICUs[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2023, 13(1): 130.
doi: 10.1186/s13613-023-01225-7 pmid: 38112851 |
| [44] | Huang C. Gender differences in prolonged mechanical ventilation patients-A retrospective observational study[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2022, 15: 5615-5626. |
| [45] | Röser E, Michels-Zetsche JD, Ersöz H, et al. Differences between women and men in prolonged weaning[J]. Respir Res, 2024, 25(1): 363. |
| [46] | Chuang CY, Hsu HS, Chen GJ, et al. Underweight predicts extubation failure after planned extubation in intensive care units[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(4): e0284564. |
| [47] |
Fujinaga J, Suzuki E, Irie H, et al. Body mass index and ventilator dependence in critically ill subjects in Japan: A cohort study using a nationwide database[J]. Respir Care, 2021, 66(9): 1433-1439.
doi: 10.4187/respcare.08660 pmid: 33688093 |
| [48] |
Song J, Luo Q, Lai X, et al. Combined cardiac, lung, and diaphragm ultrasound for predicting weaning failure during spontaneous breathing trial[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2024, 14(1): 60.
doi: 10.1186/s13613-024-01294-2 pmid: 38641687 |
| [49] | 黄光成, 周良, 石建伟, 等. 机器学习算法在疾病风险预测中的应用与比较[J]. 中国卫生资源, 2020, 23(4): 432-436. |
| [1] | Xu Huifeng, Jin Yanyong, Gou Ruolan, Hu Mingzhe. Risk factors for hydrocephalus in children with cerebral hemorrhage and its prediction model [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(4): 325-328. |
| [2] | Zhao Guangyan, Han Tuo, Liang Xiying, Wang Qian, Zhang Yan, Wang Congxia. Risk factors and predictive model for masked hypertension in young and middle-aged adults [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(3): 205-210. |
| [3] | Li Dengfeng, Huang Jiahu, Li Tingjun, Lv Yong, Jin Zhenzhen, Lian Shaofeng. Construction of a prediction model for refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children based on lung ultrasound score [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 153-157. |
| [4] | Liu Jinteng, Liu Xingyu, Huang Lumei, Pan Hailong. The risk prediction models for pneumonia in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(1): 5-13. |
| [5] | Zhu Jieyun, Gao Min, Huang Chunli, Pan Dongzan, Wang Qiaoyan, Lu Zhao. Risk prediction model for readmission of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 773-779. |
| [6] | Wang Caizhen, Miao Lina, Chen Yuan, Li Shuangcheng. Effectiveness of high-frequency vagus nerve stimulation in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 593-597. |
| [7] | Zhang Zhiping, Zhang Baomin, Qin Wei, Gao Lingjie, Chen Dong. Clinical application of nutritional support on mechanical ventilation in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(6): 510-514. |
| [8] | Song Siping, Jiang Qixia, Liu Xiaoqing. Risk factors of intraoperative acquired pressure injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 211-219. |
| [9] | Lyu Yixuan, Lu Zhanfei, Sun Nianzhe, Li Fuhan, Liu Rong. Systematic review on the efficacy of dual-energy CT and ultrasound in the diagnosis of gout [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(1): 5-7. |
| [10] | Zhang Junkaia, Xing Yunfeia, Mai Pujieb, Liu Ningninga, Yang Nannana. Effect of early enteral nutrition support on critically ill patients treated with mechanical ventilation [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(3): 251-254. |
| [11] | Chen Xianrui, Wen Hong, Huang Jianqi, Guo Biyun, Bai Haitao, Wu Jinzhun. Relationship between ARID5B gene rs10821936 polymorphism and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a systematic and metaanalysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(3): 197-205. |
| [12] | Hu Guang1, Liu Zihan1, Du Linjiao1, Wei Yuna1, Zeng Ming2. Efficacy and safety of umeclidinium/inhaled corticosteroid/ longacting β2agonist in treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a metaanalysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(1): 77-84. |
| [13] | Fang Mingxing;Liu Na;Huang Qingsheng;Zhang Lixia;Wu Chuntao;Zhang Huawei;Li Yan;Guo Jianying;Dong Shimin;Wang Zhiyong. Multifactor analysis of postoperative mechanical ventilation supporting time in patients with orthotopic liver transplantation [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(6): 667-669670. |
| [14] | Zhang Zhen;Jia Shiqiang;Peng Zhanxian;Zong Wei;Wen Shiwei;Sun Luhua;Rong Xuebing;Wang Jingjun;Dong Shimin. Clinical value of rapid shallow breathing index in predicting ventilator weaning in sleeping patients with acute exacerbation chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(5): 506-508509. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||